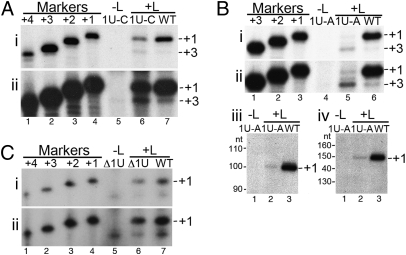
Fig. 3.
Effect of the 3′ terminal mutations on initiation site selection. Primer extension analysis of the RNA generated from the 1U-C, 1U-A, and Δ1U mutant minireplicons (A, B, and C, respectively). In each case, the mutant RNA was compared with RNA generated from a WT minireplicon. In i and ii, the primer hybridized at positions 24–48 relative to the +1 initiation product. Lane 4 or 5 (as indicated) is a negative control of RNA from cells transfected with plasmid encoding the relevant mutant minireplicon but no L polymerase plasmid. Molecular weight markers present in lanes 1–3 or 1–4 are end-labeled primers, representing products initiated from positions +3 to +1 or +4 to +1 of the template, respectively. In each case, ii is a longer exposure of the gel shown in i to show the +3 initiations. (B iii and iv) Primer extension analysis of the same RNA samples as shown in i and ii, using primers that hybridized at positions 74–100 (iii) or 124–148 (iv) relative to the 5′ end of the +1 initiation product.