Fig. 1.
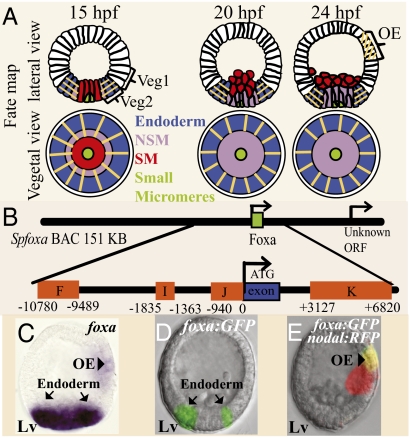
Expression and regulatory structure of the foxA gene. (A) Lineage fate map showing lateral and vegetal views at 15, 20, and 24 hpf. The orange lines indicate the domains where foxa is expressed. Green, small micromeres; red, SM; purple, veg2 NSM; blue, veg2 endoderm; white, veg1 and the ectoderm; OA, oral ectoderm. (B) Diagram of foxA CRMs (orange boxes) in SpfoxA BAC. The numbers on the CRMs edges indicate their distance from foxA start of translation. foxA single exon is marked as a blue box. (C) Whole mount in situ hybridization of foxa at 24 hpf. foxa is expressed in the endoderm (arrows) and in the oral ectoderm (arrowhead). (D and E) Expression of foxA:GFP BAC at 24 hpf. The reporter is expressed in the endoderm (D) and in the oral ectoderm (E). Because the oral and aboral sides of the embryo are indistinguishable at 24 hpf, we coinjected the foxa:GFP BAC with Nodal:RFP BAC, which is expressed in the oral ectoderm. The figure shows the overlay of the two flourophores. Lv, lateral view.