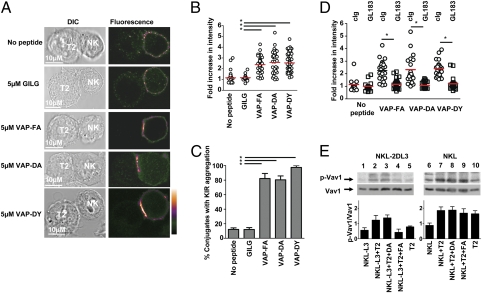
Fig. 5.
The weak KIR-binding peptide VAP-DA mediates KIR clustering at the interface between NK cells and target cells. (A) Clustering at the interface between NKL-2DL3 cells and T2 targets in the absence of peptide or in the presence of the indicated peptides. Images are labeled with a pseudocolor scale. (B) The increase in fluorescence intensity at the interface between NKL-2DL3 and the T2 cells compared with the NKL plasma membrane at a noncontact area (means are indicated in red). (C) The percentage of conjugates with KIR clustering depicted as the means and SDs from three independent experiments. A minimum of 17 conjugates were counted per condition per experiment. (D) The effect of addition of GL183 on clustering between peptide pulsed T2 cells and NKL-2DL3. In all panels, an asterisk indicates a significant difference of P < 0.0001 (Student t test). (E) Western blot analysis of KIR2DL3 transfected NKL (Left) or untransfected NKL (Right) cells incubated with T2 cells unloaded (lanes 2 and 7) or loaded overnight with the peptides VAP-DA (lanes 3 and 8) and VAP-FA (lanes 4 and 9) at 20 μM and then analyzed for the presence of absence of VAV1 and phosphorylated VAV1. Baseline signals from NKL-2DL3 (lane 1), NKL-2DL3 (lane 6), and T2 cells (lanes 5 and 10) are also shown. The mean quantitation of the ratio of pVAV1 to VAV1 from three independent experiments ± SEM is shown graphically.