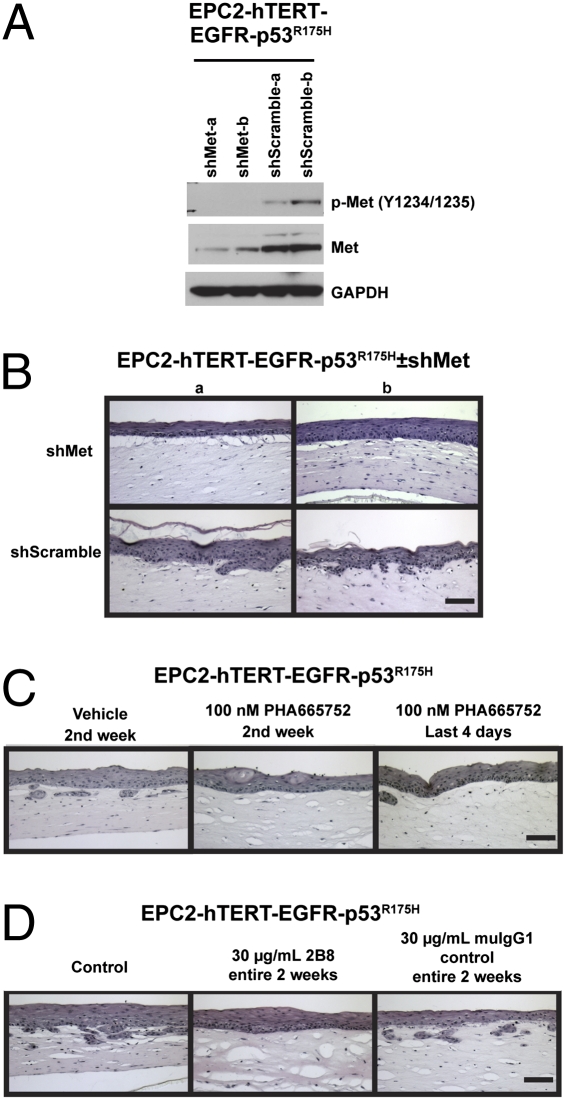
Fig. 6.
Inhibition of HGF/Met pharmacologically or by genetic knockdown in transformed esophageal epithelial cells reduces invasion. (A) Western blot of EPC-hTERT-EGFR-p53R175H-shMet or EPC-hTERT-EGFR-p53R175H-shScramble cells (two independent lines of each genotype) to determine extent of Met knockdown of total protein and activation state. (B) H&E-stained sections of organotypic culture of EPC-hTERT-EGFR-p53R175H-shMet or EPC-hTERT-EGFR-p53R175H-shScramble cells seeded above matrices containing FEF3 fetal esophageal fibroblasts. (C) H&E-stained sections of organotypic cultures of EPC-hTERT-EGFR-p53R175H cells seeded above FEF3 matrices treated with DMSO vehicle (days 7–15) or 100 nM PHA665752 (days 7–15 or day 11–15) as indicated. (D) H&E-stained sections of organotypic cultures of EPC-hTERT-EGFR-p53R175H cells seeded above FEF3 matrices treated with 30 μg/mL 2B8 or muIgG1 control antibody (days 0–15) as indicated. (Scale bars: 100 μm.)