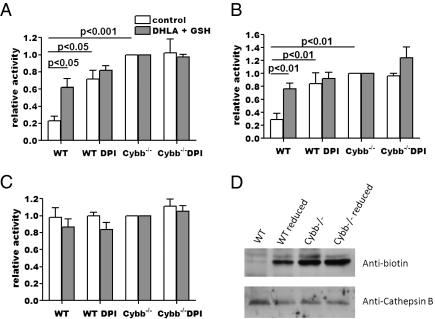
Fig. 4.
NOX2 inactivates phagosomal cysteine cathepsins via a reversible oxidative modification. Aspartic and cysteine cathepsin activities of phagosomes isolated from WT and Cybb−/− BMMØs ± 0.5 μM DPI were measured fluorometrically in vitro, with or without reduction by 1 μM DHLA and 30 mM GSH. (A–C) Relative activities were determined by the rate of increase in fluorescence of cathepsin-specific fluorogenic substrates at 37 °C, pH 5.5 and expressed relative to the corresponding Cybb−/− samples. (A) Cathepsin B (cysteine cathepsin); (B) cathepsin S (cysteine cathepsin); (C) cathepsin D/E (aspartic cathepsins). Graphs represent data from three independent experiments. Error bars denote SEM. P values were determined by ANOVA. (D) Relative proportions of active cathepsin B in phagosomes isolated from WT and Cybb−/− BMMØs were determined by reaction with the cathepsin B-specific biotinylated irreversible inhibitor biotin-FA-FMK with or without reduction by DHLA and GSH. Western blot images depict active (biotinylated) and total cathepsin B.