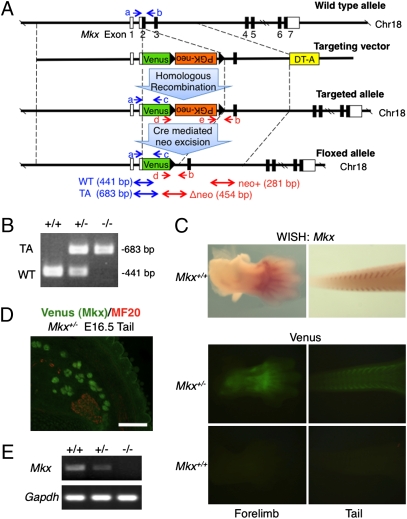
Fig. 1.
Generation of Mkx mutant mice. (A) Diagram of the Mkx targeting construct. Blue and red arrows (a–e) show genomic PCR primers for genotyping. White box, UTR; Black box, coding region; DT-A, diphtheria toxin A; WT, wild-type allele; TA, targeted allele. (B) Genomic PCR of wild-type and Mkx mutant mice for genotyping using primers a, b and c. (C) Whole-mount in situ hybridization of Mkx (Upper) and whole-mount visualization of Venus signals (Lower) in E13.5 forelimb and tail of wild-type or Mkx mutant embryos. (D) Immunohistochemistry for anti-myosin heavy chain (MF20; red) and visualization of Venus in cryosection of E16.5 tail of a Venus knockin Mkx heterozygous embryo. (Scale bar, 100 μm.) (E) RT-PCR analysis for Mkx and Gapdh of Achilles tendon in wild-type and Mkx mutant mice.