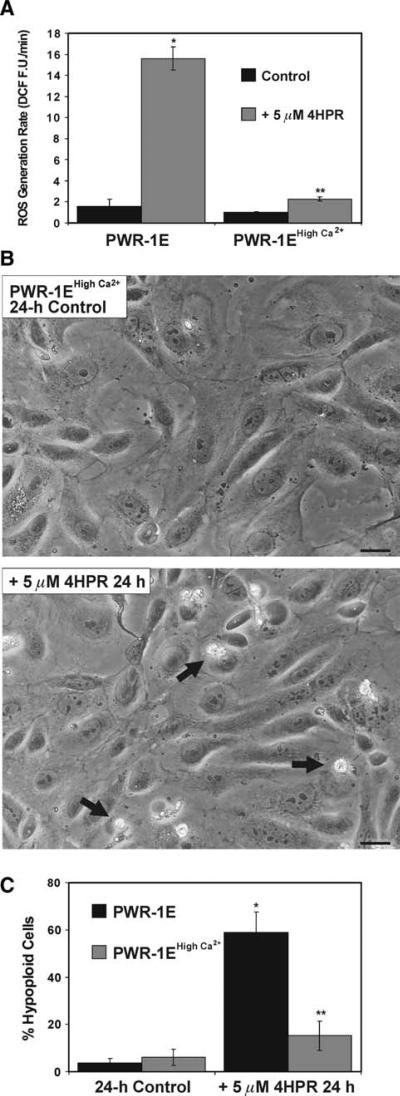
Fig. 4.
PWR-1E cells cultured in high Ca2+ KGM exhibit reduced sensitivity to 4HPR-induced ROS and apoptosis. a PWR-1E cells were cultured in 6-well tissue culture plates as described in Fig. 2a. The cells were exposed for 2.5 h to 5 μM 4HPR or an equal volume of the vehicle Me2SO (control), and examined for the oxidation of 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin to DCF using a microplate spectrofluorimeter. ROS generation rates (fluorescence units/min, FU/min) were derived from the slopes of lines obtained between 30 and 120 min from triplicate wells in 6-well tissue culture plates. The results are expressed as the mean of triplicate samples for each treatment ± SD (error bars)(* P < 0.001 PWR-1E cells cultured in KGM and treated with 4HPR compared to their control, ** P < 0.01 compared to the PWR-1E cells cultured in KGM and treated with 4HPR). b Images showing PWR-1E cells cultured in KGM with 1.9 mM Ca2+ (i.e., PWR-1E high Ca2+) exposed to Me2SO (control) or 5 μM 4HPR for 24 h. The remnants of apoptotic cells in the 4HPR-treated culture are indicated with arrows. The floating cells are not seen in the photographs because the culture medium was removed prior to imaging. The scale bars equal 18 μm. c A summary of the hypoploid DNA content for cells examined in the experiments described in b. The results are expressed as a percentage of the mean hypoploid cells detected in triplicate samples for each treatment ± SD (error bars) (* P < 0.001 PWR-1E cells cultured in KGM and treated with 4HPR compared to their control, ** P < 0.01 compared to the PWR-1E cells cultured in KGM and treated with 4HPR)