Figure 5.
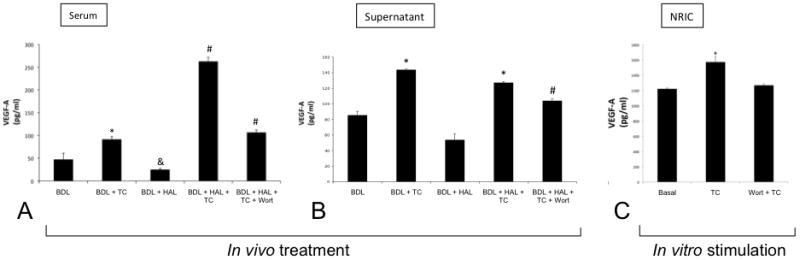
[A-B] Taurocholic acid feeding increased the levels of VEGF-A in the serum and cholangiocyte supernatant of BDL rats. VEGF-A levels were reduced in the serum and cholangiocyte supernatant of BDL rats by HAL, decreases that were prevented by TC feeding. TC prevention of HAL-induced decreases of VEGF levels in serum and cholangiocyte supernatant were blocked by wortmannin. Data are mean ± SE of 4 experiments *p < 0.05 vs. BDL. &p< 0.05 vs. BDL. #p < 0.05 vs. all the other groups. [C] In vitro treatment of NRIC with taurocholic acid (20 μM) for 24 hours induced an increase of VEGF-A levels in the supernatants collected from NRIC compared to basal NRIC: TC-induced increase in NRIC VEGF-A levels was blocked by preincubation with wortmannin. Data are mean ± SE of 4 experiments. *p < 0.05 vs. basal. BDL = bile duct ligated; HAL = hepatic artery ligation; TC = taurocholic acid; Wort = Wortmannin.
