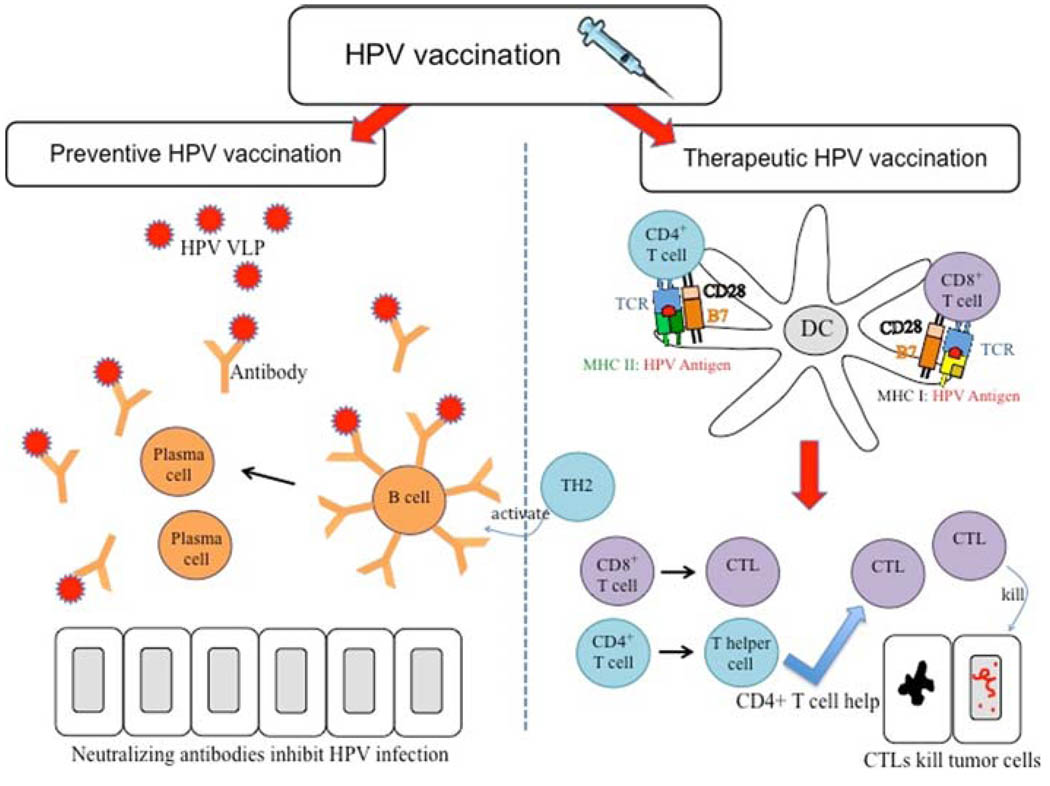
Fig. 1.
HPV vaccination. Vaccination can be categorized into two categories: preventive and therapeutic vaccination. Preventive HPV vaccines focus on the humoral immunity. Preventive HPV vaccines deliver HPV virus-like particles (VLPs) encoding L1 and/or L2 viral capsid proteins. B cells bind to the HPV VLPs and are activated by TH2 (differentiated CD4+ T helper cells) to become plasma cells, which secrete antibodies. These neutralizing antibodies block primary HPV infection, inducing protection against HPV. Therapeutic HPV vaccination focuses more on cell-mediated immunity. Cell-mediated immunity involves the interaction between professional antigen-presenting cells, particularly dendritic cells and T cells. Dendritic cells present the MHC:peptide complex to T cells and prime naїve T cells to become effector CD4+ T cells, if presented via MHC class II, or effector CD8+ T cells, if presented via MHC class I. These effector T cells mediate therapeutic effects, with effector CD8+ T cells, also known as cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) mediating antigen-specific killing of tumor cells, and effector CD4+ T cells differentiating into T helper cells to either augment CTL immune response or activate B cells to make antibodies