Figure 1.
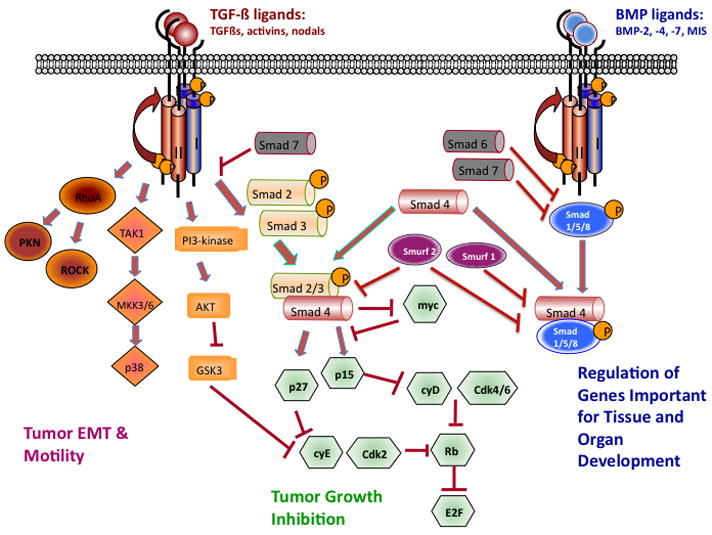
The TGF-β ligands signal through the type I and type II TGF-β receptors. Canonical signaling proceeds with phosphorylation of SMAD2 and SMAD3, which then combine with SMAD4 to enter the nucleus and mediate growth inhibition. TGF-β binding to its receptors activates many non-canonical signaling pathways, including small GTPases (RhoA, PKN, and Rock), p38 kinase and PI3 kinase pathways. These pathways are important in regulating tumor-cell migration and metastasis. In addition, bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) signal through SMAD1, SMAD5 or SMAD8, which form complexes with SMAD4, which activate or repress targeted gene transcription that is important for tissue and organ development. Smad 6 and 7 are negative mediators in the TGF-β signaling pathway.
