Figure 4.
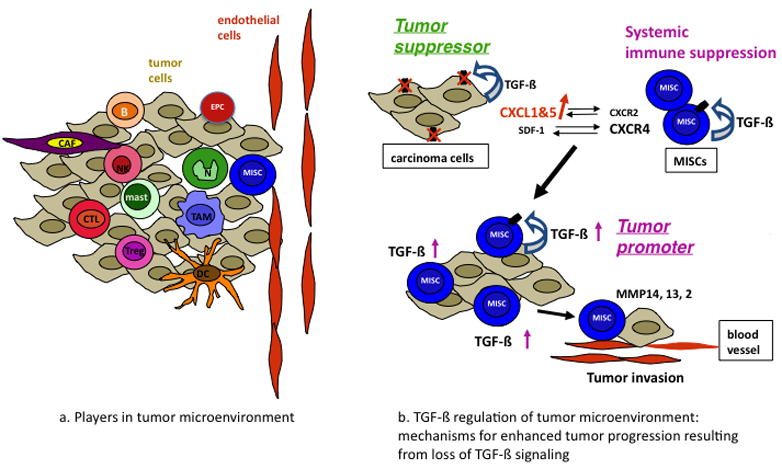
TGF-β regulation of tumor microenvironment. (a) Cellular players in tumor microenvironment. (b) The mechanisms by which TGFβ signaling switches from a tumor suppressor to a tumor promoter are shown. TGFβ signals through the type II receptor mediate growth inhibition of carcinoma cells. When TβRII is deleted or downregulated, the result is increased chemokine/chemokine-receptor signaling, such as CXCL1–CXCL5/CXCR2 and SDF-1–CXCR4. Host-derived immature myeloid Gr-1+CD11b+ cells are recruited into the tumor microenvironment through these chemokine mechanisms. These Gr-1+CD11b+ cells express high level of MMPs and TGFβ1, which promote tumor invasion and immune suppression. The effect of Gr-1+CD11b+ cells on the tumor microenvironment and host immune surveillance constitute a tumor-promoting mechanism of TGFβ signaling.
