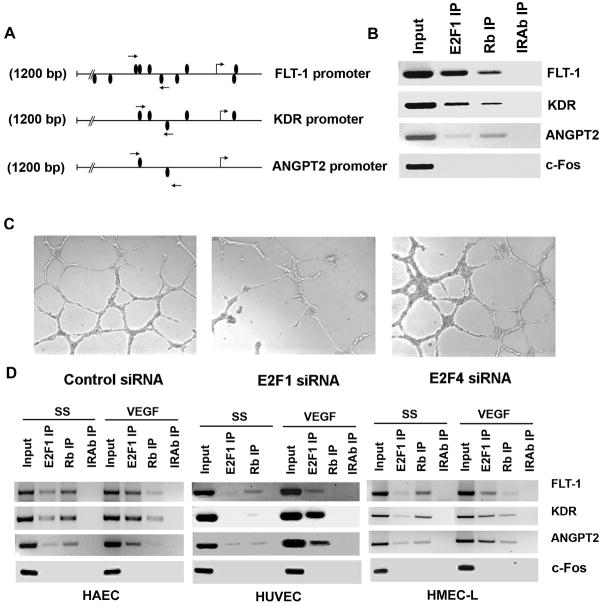
Figure 1.
(A) A schematic representation of FLT-1 promoter, KDR promoter and Angiopoietin 2 promoter showing the potential E2F binding sites. Position of primers used for ChIP assay spanning the putative E2F binding sites are shown as arrows. (B) E2F1 and Rb associates with FLT-1, KDR and ANGPT2 promoters in vivo. ChIP assays were carried out on asynchronously growing HAECs. Input indicates an aliquot of total DNA. Antibodies used for immunoprecipitation are indicated above the lanes. (C) Depletion of E2F1 by transfecting HAECs with siRNA targeted to E2F1 abrogates angiogenic tubule formation while non-targeting siRNA and E2F4 siRNA did not affect the formation of angiogenic tubules. HAECs were transfected with the indicated siRNAs and plated on matrigel using standard protocols and observed under light microscopy. (D) VEGF induces recruitment of E2F1 on FLT-1, KDR and ANGPT2 promoters. ChIP assay was carried out on serum starved and VEGF stimulated HAEC, HUVEC and HMEC-L cells. In serum starved cells, a significant amount of Rb was found to be associated with these promoters. VEGF stimulation induced the binding of E2F1 to the promoter region while dissociating Rb in all the three cell types tested.