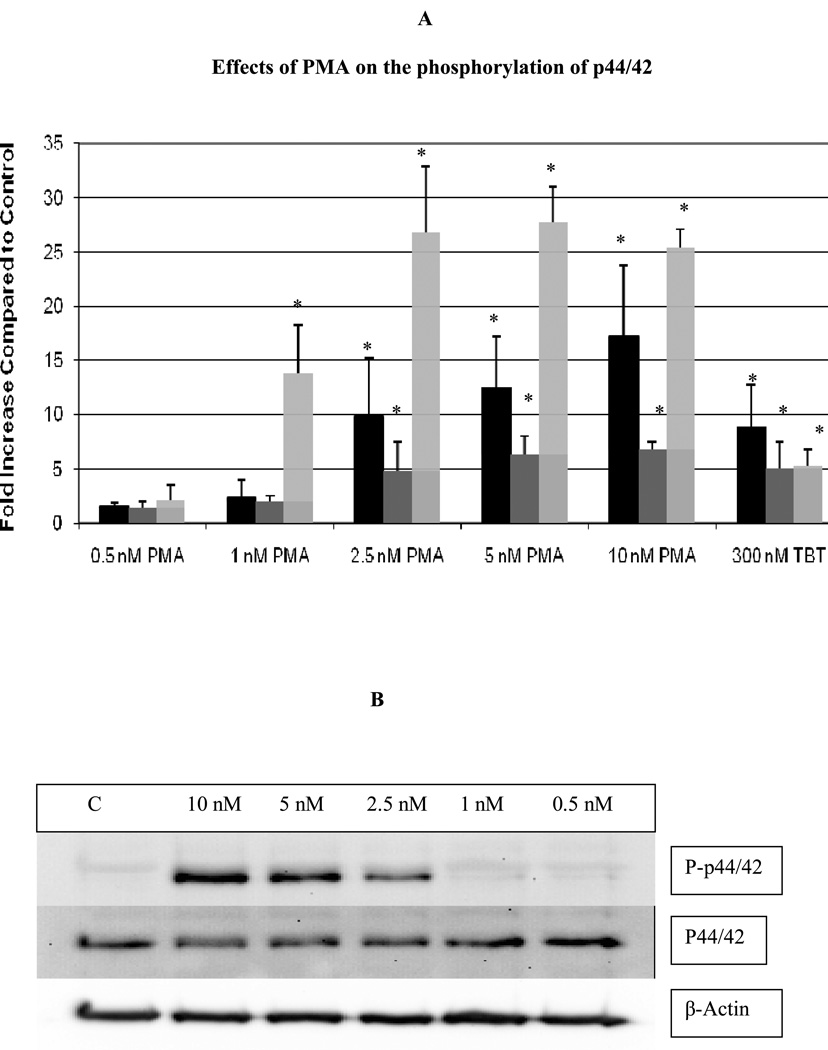
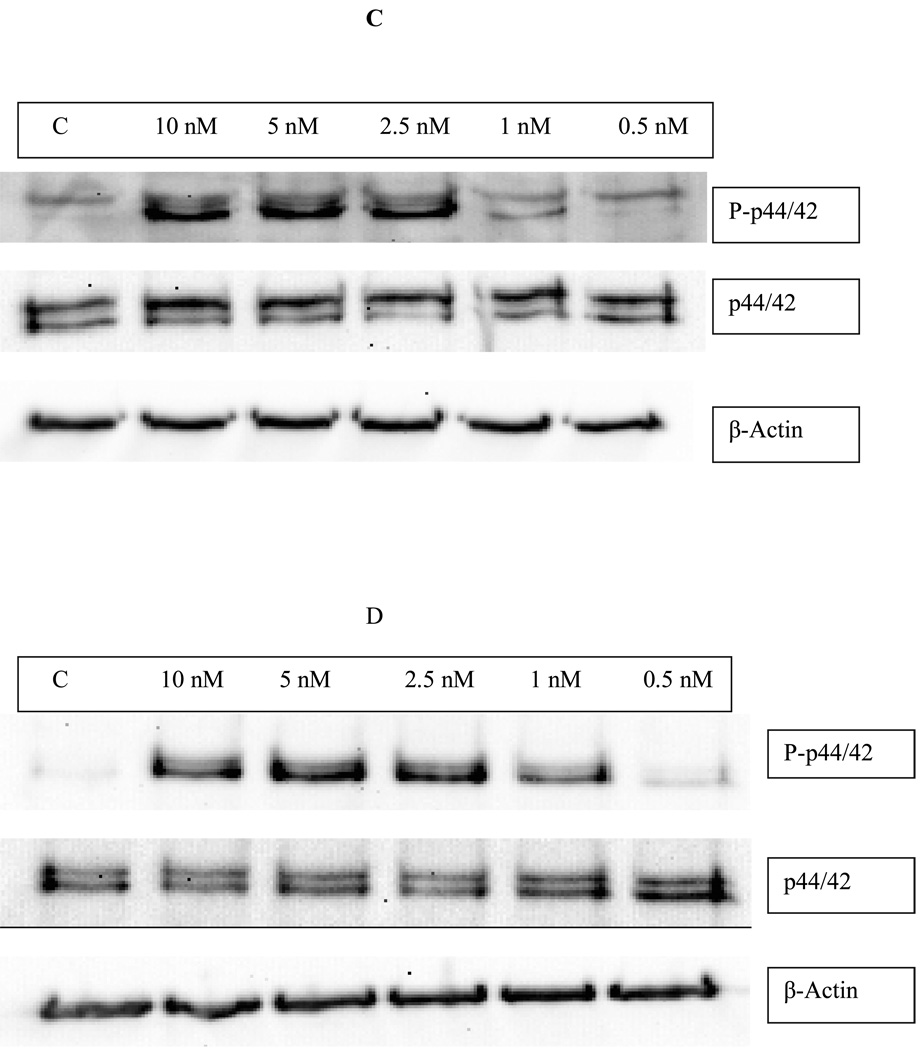
Figure 2.
Effects of exposures of human NK cells to PMA on the phosphorylation state of p44/42. A) Fold increase in phospho-p44/42 as compared to control cells following 10 min (black bar), 1 hour (dark gray bar), and 6 hour (light gray bar) exposures to varying concentrations of PMA or to 300 nM TBT. Values are mean ±S.D. from at least three separate experiments using different donors (triplicate determinations for each experiment, n ≥ 9). An asterisk indicates a significant increase as compared to control (p<0.05). B) Representative western blot of the effect of 10 min exposures of NK cells to PMA on the phosphorylation state of p44/42. C) Representative western blot of the effect of 1 h exposures of NK cells to PMA on the phosphorylation state of p44/42. D) Representative western blot of the effect of 6 h exposures of NK cells to PMA on the phosphorylation state of p44/42.