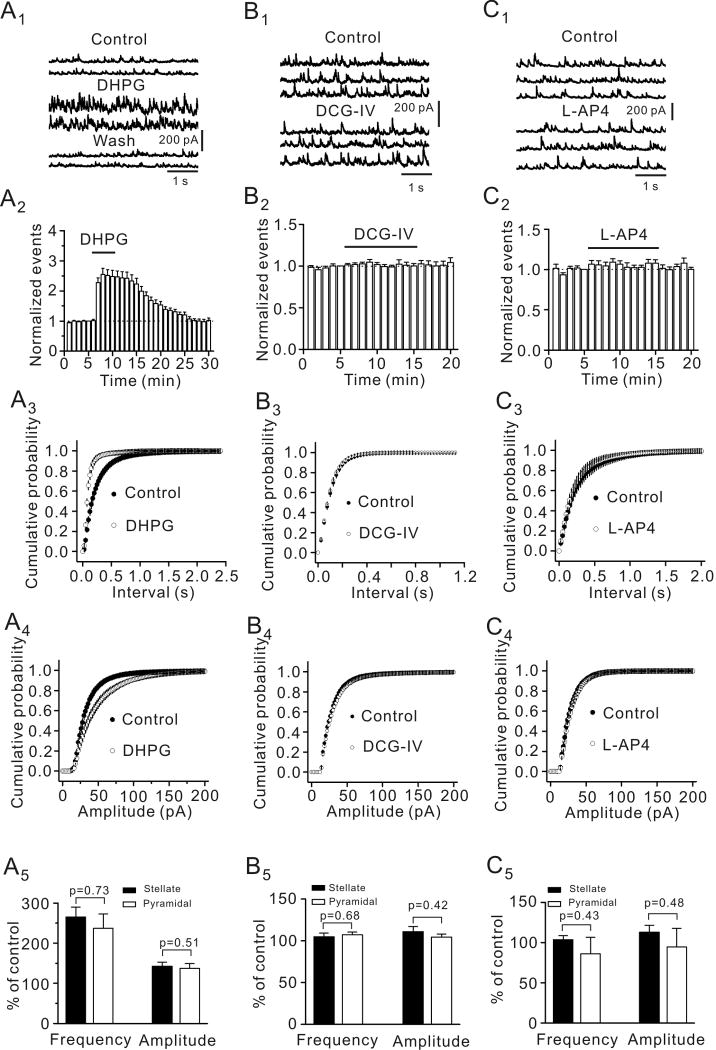
Fig. 1.
Activation of group I (A1-A5) not group II (B1-B5) and group III (C1-C5) mGluRs increases the frequency and amplitude of sIPSCs recorded from principal (stellate and pyramidal) neurons in the EC. A1, sIPSCs recorded from a stellate neuron before, during and after the application of the group I mGluR agonist, DHPG (10 μM). A2, DHPG increased sIPSC frequency (n=21, p<0.001, two-way ANOVA). A3, Cumulative probability of sIPSC frequency before and during the application of DHPG (n=21, p<0.001, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test). A4, Cumulative probability of sIPSC amplitude before and during the application of DHPG (n=21, p=0.001, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test). A5, DHPG increased sIPSC frequency and amplitude in stellate (n=13) and pyramidal (n=8) neurons equally (unpaired t-test). B1-B5, Application of the group II mGluR agonist, DCG-IV (10 μM) failed to change significantly sIPSC frequency and amplitude (n=10). The figure was arranged in the same way as A1-A5 and the same kinds of statistical analysis methods were used. C1-C5, Application of group III mGluR agonist, L-AP4 (10 μM) failed to change sIPSC frequency and amplitude (n=10). The figure was arranged in the same fashion and the same kinds of statistical analysis methods were used.