Fig 4.
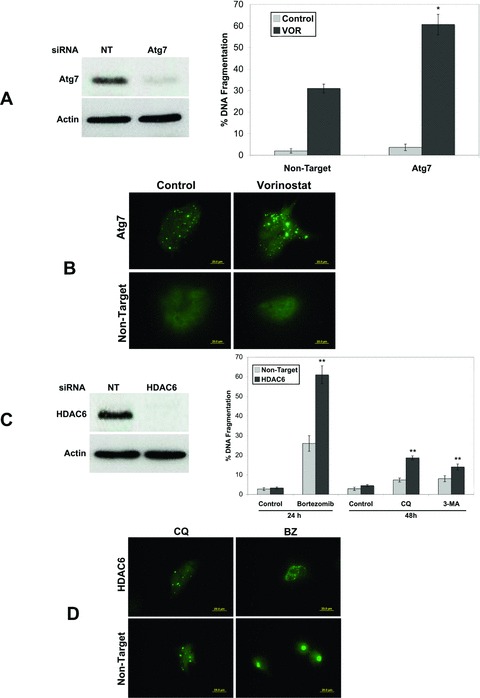
Role of Atg7 and HDAC6 in CQ+VOR-mediated apoptosis. (A) Atg7 knockdown enhances VOR-induced apoptosis. RNAi was performed as described in ‘Materials and methods’ and immunoblotting confirmed knockdown of Atg7. HCT8 cells transfected with non-target or Atg7 siRNA were treated with VOR for 48 hrs. Apoptosis was determined by PI staining and flow cytometry. Mean ± S.D., n= 3. *Indicates significant difference from non-target siRNA transfected cells treated with BZ. P < 0.05. (B) Knockdown of Atg7 causes ubiquitinated aggregate accumulation, which is enhanced by VOR. Following knockdown of Atg7 by RNAi, cells were treated with VOR for 48 hrs. Aggregate formation was determined by staining with an anti-ubiquitin antibody and images were captured by fluorescent microscopy. (C) Knockdown of HDAC6 enhances BZ-induced apoptosis, but only marginally increases CQ or 3-MA-mediated apoptosis. HCT8 cells were transfected with non-target or HDAC6 siRNA. Immunoblotting confirmed a decrease in HDAC6 levels. Cells were then treated with 100 nM BZ for 24 hrs or 50 μM CQ or 5 mM 3-MA for 48 hrs in the presence or absence of HDAC6 siRNA. Apoptosis was determined by PI staining and flow cytometry. Mean ± S.D., n= 3. **Indicates significant difference from non-target siRNA transfected cells treated with the same agent. P < 0.05. (D) Knockdown of HDAC6 disrupts BZ-mediated aggresome formation, but does not alter CQ-induced aggregate localization. Following knockdown of HDAC6 by RNAi, cells were treated with CQ or BZ for 48 and 24 hrs, respectively. Aggregate accumulation was detected by staining with an anti-ubiquitin antibody as described in the ‘Materials and methods’.
