Fig 5.
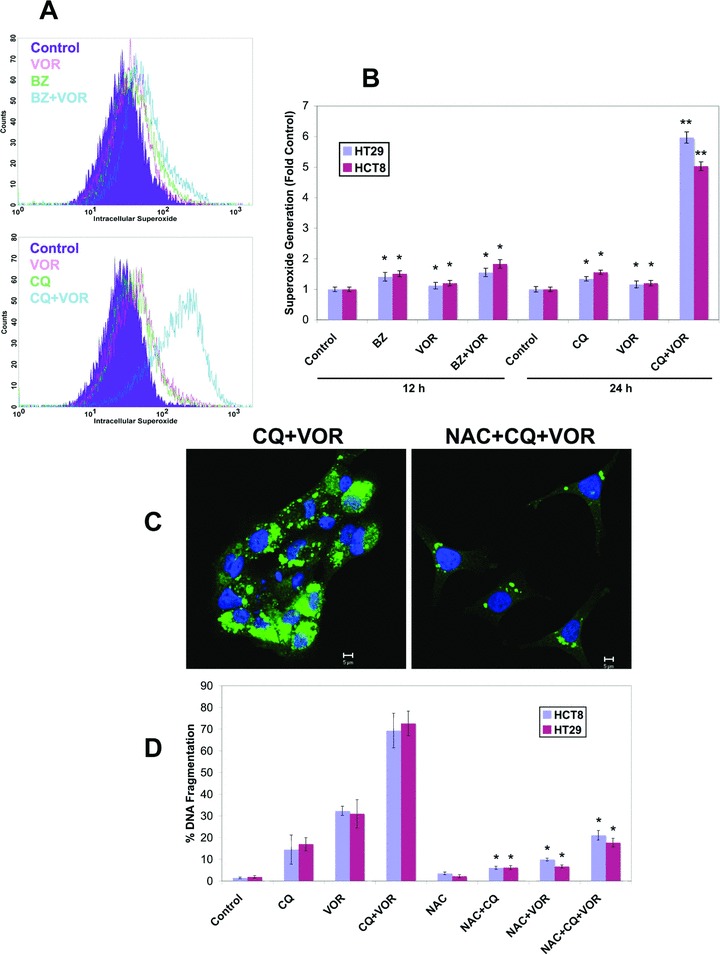
Treatment with the CQ/VOR combination stimulates a strong increase in superoxide production that contributes to ubiquitinated aggregate accumulation. (A) Flow cytometric analysis of superoxide content in HT29 cells treated with 100 nM BZ, 2.5 μM VOR, or both for 12 h, or 50 μM CQ, 2.5 μM VOR, or the combination for 48 hrs. Cells were labelled with hydroethidine (100 ng/ml) for 1 h and analyzed by flow cytometric analysis. (B) The CQ/VOR combination induces a strong increase in superoxide production. HCT8 and HT29 cells were treated with the 100 nM BZ, 2.5 μM VOR, 50 μM CQ or combinations for the indicated times. Cells were stained with hydroethidine and analyzed by flow cytometry. Mean ± S.D., n= 3. *Indicates significant difference from the control group. **Indicates a significant difference from single agent treatment groups. P < 0.05. (C) The antioxidant NAC reduces the levels of ubiquitinated aggregates. Cells were treated with 50 μM CQ and 2.5 μM VOR for 48 hrs with or without 10 mM NAC. Ubiquitinated aggregates were visualized with an anti-ubiquitin antibody (green). The nucleus was counterstained with ToPro-3 (blue). Images were generated by confocal microscopy. (D) Treatment with NAC strongly reduces apoptosis stimulated by the CQ/VOR combination. HT29 and HCT8 cells were treated with 10 mM NAC, 50 μM CQ, 2.5 μM VOR, or combinations for 48 hrs. Apoptosis was measured PI staining followed by flow cytometry. Mean ± S.D., n= 3. *Indicates a significant difference from cells treated without NAC. P < 0.05.
