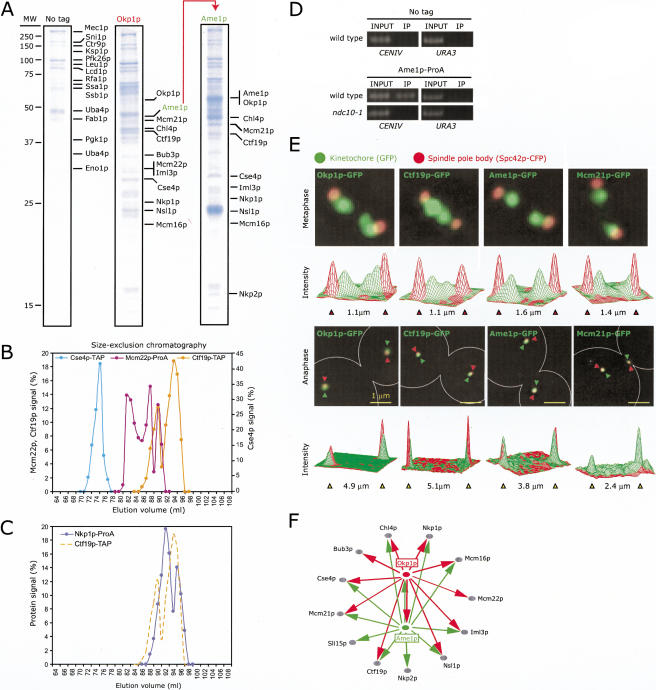
Figure 2.
Purification and identification of kinetochore proteins associated with Okp1p and Ame1p. (A) Left lane shows a colloidal blue-stained SDS PAGE gel of a mock immune purification from a wild-type strain (no tag). The labeled proteins are commonly found as contaminants in single-step affinity purifications from yeast. The center and right lanes are purifications from the Okp1p-3FLAG and Ame1p-3FLAG strains. Proteins that were highly enriched and absent in the control are labeled. The positions of some proteins differ from the expected molecular weights (Suppl. Table 2) as a consequence of protein degradation. (B) Hydrodynamic analysis of Ctf19p-TAP on size-exclusion chromatography compared to Cse4p-TAP, Mcm22p-ProA, and (C) Nkp1p-ProA. (D) Crosslinking of Ame1p-ProA to CENIV DNA in wild-type or ndc10-1 cells at 37°C using ChIP. DNA in immune complexes (IP) was amplified with primers to CENIV, or as negative controls, TELVI-R and URA3, and compared to DNA in whole-cell extracts (labeled “1% INPUT”). (E) Images of metaphase (upper panels) and anaphase (lower panels) cells carrying Spc42p-CFP (red) and Okp1p-GFP, Ctf19p-GFP, Ame1p-GFP, or Mcm21p-GFP (green). Images represent projections of 3D image stacks containing 10 to 20 0.2-μm sections and collected on a DeltaVision deconvolution microscope. The graphs show the intensity of the CFP (red) and GFP (green) signals along the axis of the spindle in arbitrary units. (F) Network summarizing interactions found among proteins present in Okp1p and Ame1p immune purifications (see Suppl. Table 2 for further information).