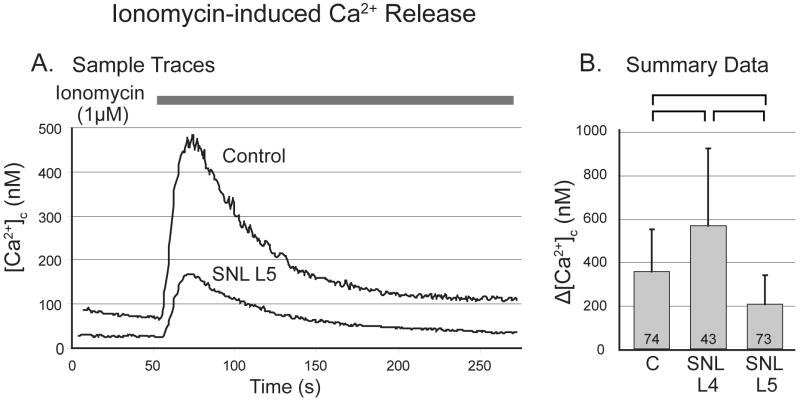
Figure 4.
Response of cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]c) in sensory neurons to application of ionomycin in bath solution not containing Ca2+. A. Sample traces from a control (C) neuron and another from the fifth lumbar (L5) dorsal root ganglion after spinal nerve ligation (SNL). B. Application of ionomycin produces transients with reduced amplitude in L5 neurons, but increased amplitude in L4 neurons (one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc testing). Numbers in the bars indicate n for number of neurons, brackets above bars connect groups that are significantly different (P<0.05), and error bars show standard deviation.