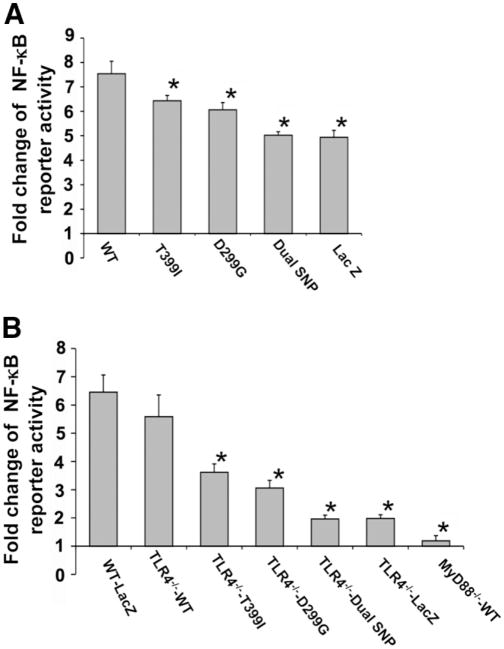
Fig. 2.
TLR4 SNPs confer decreased NF-κB activation to LPS stimulation in HSCs. An NF-κB responsive reporter plasmid was cotransfected with TLR4 cDNAs into LX-2 cells or transfected into mHSCs stably reconstituted with human TLR4 cDNAs. The cells were stimulated with LPS (100 ng/mL) for 12 hours. The activation of NF-κB responsive reporter was determined with a dual-luciferase reporter assay system. (A) Fold change of NF-κB reporter activity in LX-2 cells transfected with TLR4 WT or SNP sequences, or a LacZ control vector. (B) Fold change of NF-κB reporter activity in TLR4−/− mouse HSCs transfected with TLR4 WT or SNP sequences, or a LacZ control vector, and in MyD88−/− HSCs reconstituted with WT human TLR4 sequence. Cells expressing either the single or dual SNPs had less NF-κB activation. Each column represents the mean ± SEM of n = 6 per group in more than three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 when compared with the WT TLR4 cDNA-transfected stellate cells.