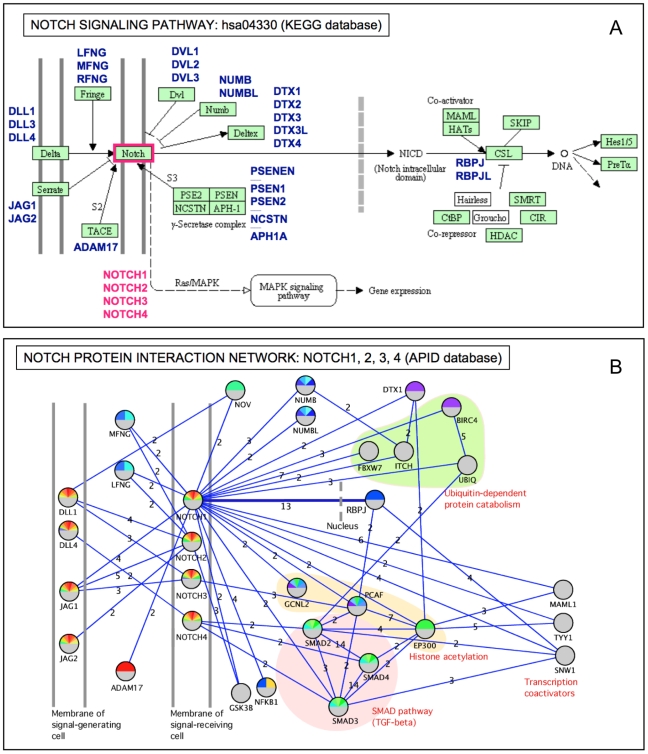
Figure 3. A network derived from PPIs compared to the related canonical pathway.
Comparison between a known pathway (NOTCH signaling pathway, taken from the KEGG database, ID: hsa04330) and the corresponding interactome network build using the proteins that interact with human NOTCH proteins. The top panel (A) shows the pathway including nine proteins (green boxes) directly connected to NOTCH. In this pathway, the central element is the NOTCH receptor and the interaction of its intracellular domain (called NICD) with protein RBPJ. The bottom panel (B) shows the NOTCH PPI network (built with Cytoscape and APID2NET), including all interactors proven with at least two different experiments. The number of experiments is indicated next to each link (blue line). The PPI network provides complementry information to the KEGG pathway, revealing the particular links of each of the four NOTCH paralogous proteins (NOTCH1, 2, 3, and 4) present in the human proteome. The biomolecular elements included in both networks are quite similar and the information that can be deduced from them is complementary. This can be seen in the interaction between NOTCH and RBPJ that drives the central signaling of the pathway and it is present in both networks.