Figure 3.
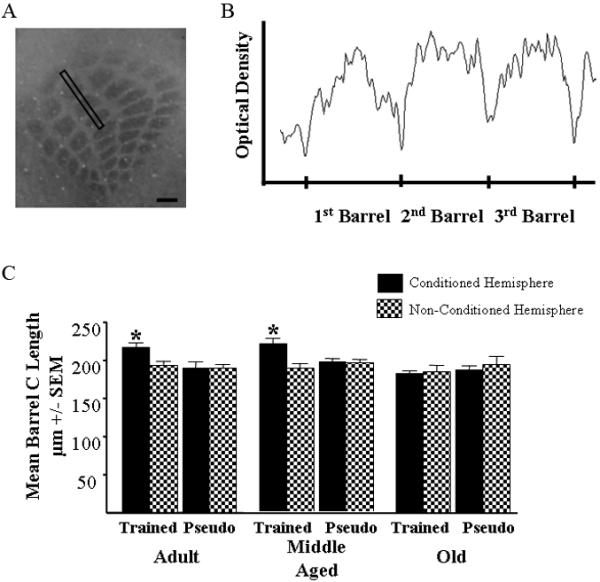
Metabolic expansion of conditioned barrels is dependent upon acquisition of the WCS-trace association. A) Illustration of a cytochrome oxidase stained cortical barrel field with a sampling area over the C row. Scale bar = 200μm. B)Illustration of an optical density histogram of the row of barrels outlined in the barrel field illustrated in A. Note tic marks on the x axis delineating the point between two barrel walls. Mean barrel width was calculated by measuring the distance from the first to the third barrel and dividing by three. C) Adult and Middle Aged mice that were trained on the WCS trace paradigm exhibited an increase in the length of the metabolic neocortical barrel representation compared to the contralateral hemisphere and pseudo conditioned mice. Old mice, unable to learn the WCS trace association did not exhibit a significant increase in the length of the metabolic neocortical barrel representation compared to the contralateral hemisphere and pseudo conditioned mice. It is important to note that the Old mice learned the WCS delay association, although this caused no change in metabolic representation in the barrel cortex. Error bars = standard error of the mean (SEM). *= p<0.05
