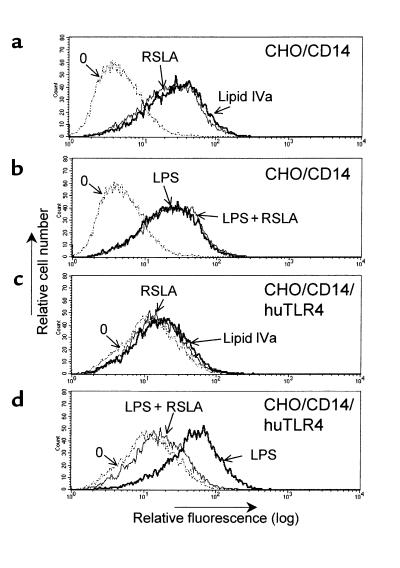
Figure 2.
RSLA blocked LPS-mediated activation in CHO/CD14 reporter cells expressing human TLR4. CHO/CD14 (a and b) and CHO/CD14/huTLR4 (c and d) reporter cells were plated in 24-well dishes. The next day, the cells were exposed to various treatments. (a and c) Cells treated with medium only (stippled lines), RSLA (5 μg/mL; thick lines), or synthetic lipid IVa (5 μg/mL). (b and d) Cells treated with medium only (stippled lines), LPS (0.5 μg/mL; thin lines) or a combination of LPS and RSLA (0.5 and 5 μg/mL, respectively) for 20 hours. After harvesting, the cells were stained for surface CD25 and subjected to flow cytometry analysis. Untreated cells (stippled lines) are indicated by “0”. The x-axis represents relative fluorescence and the y-axis represents relative cell number. One representative experiment out of 5 is shown. Note that although basal immunofluorescence in unstimulated CHO/CD14/TLR4 cells is slightly higher than in CHO/CD14 cells, the ED50 of CHO/CD14/TLR4 to LPS-induced reporter activity has been found to be identical (data not shown).