Fig 1.
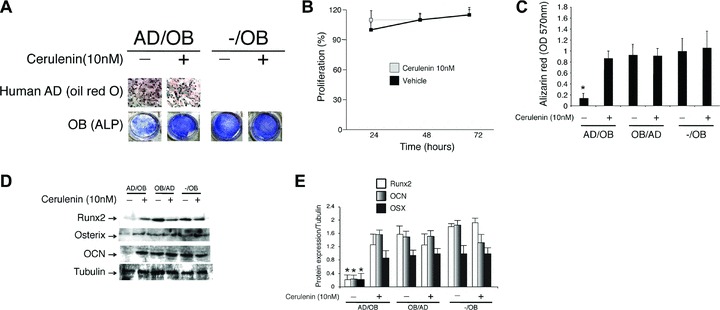
(A–C) Mature human osteoblasts were plated in co-culture with differentiating human adipocytes (AD) treated with either cerulenin (10 nM) or vehicle alone. After 3 weeks in co-culture, adipocytes were stained with oil red O (A, upper panels) to identify fat droplets and osteoblasts were stained with alkaline phosphatase (ALP) (A, lower panels) and alizarin red (C) to identify function and mineralization respectively. Addition of cerulenin to the adipocytes media did not affect adipocytes’ proliferation (B) and capacity to produce fat droplets (A, upper panels). In contrast, both osteoblast function and mineralization were significantly affected by the presence of adipocytes on top of the membrane. This inhibitory effect was prevented by addition of cerulenin (10 nM) to the media (P < 0.001). (D, E) Expression levels of Runx2, osterix (OSX) and osteocalcin (OCN) quantified by Western blot analysis were significantly reduced by the presence of adipocytes (*P < 0.001) and recovered by addition of cerulenin to the media. The data are representative of three different experiments.
