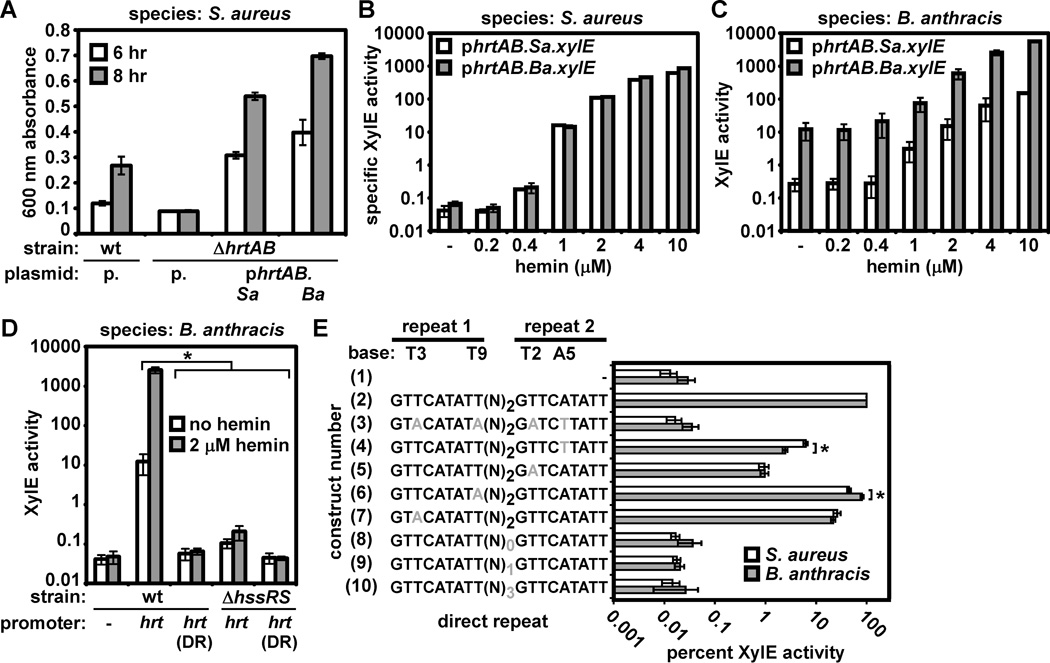
Figure 2. Elevated activity of the B. anthracis hrtAB promoter.
A. Complementation of S. aureus ΔhrtAB with S. aureus or B. anthracis hrtAB. S. aureus wildtype (wt) transformed with pOS1 (p.), ΔhrtAB with pOS1, ΔhrtAB with pOS1 encoding S. aureus hrtAB (phrtAB.Sa)), and ΔhrtAB with pOS1 encoding B. anthracis hrtAB (phrtAB.Ba) were grown in TSB + 10 µM hemin (a hemin concentration known to inhibit growth of S. aureus hss/hrt mutants). Proliferation was tracked by growth curve analysis. Culture densities at 6 hour (white bars) and 8 hour (grey bars) time points are shown. B. Reporter assay monitoring S. aureus and B. anthracis hrtAB promoter activity in S. aureus. S. aureus harboring either an S. aureus (phrtAB.Sa.xylE, white bars) or B. anthracis (phrtAB.Ba.xylE, grey bars) hrtAB promoter XylE reporter were grown without hemin (−) or in the indicated concentration of hemin and reporter activity was measured. C. Reporter assay monitoring S. aureus and B. anthracis hrtAB promoter activity in B. anthracis. Strains were grown in LB to avoid contaminating hemin in BHI. D. The dependence on HssRS and the hrtAB promoter direct repeat (DR) for constitutive and hemin-induced hrtAB promoter activity in B. anthracis. B. anthracis wildtype (wt) or ΔhssRS harboring a plasmid containing either a promoterless xylE (−, wildtype only), xylE under the control of the B. anthracis hrtAB promoter (hrt), or xylE under the control of the hrtAB promoter mutated at four conserved DR bases (hrt(DR), shown in schematic form in E, construct #3) were grown in LB (white bars) or LB + 2 µM hemin (a hemin concentration that activates the hrtAB promoter without any detectable growth inhibition of B. anthracis ΔhssRS; grey bars) and XylE activity was measured. E. Reporter assay measuring sensitivity of S. aureus and B. anthracis HssRS to perturbations in the hrtAB promoter DR. S. aureus (white bars) or B. anthracis (grey bars) harboring a promoterless xylE (construct number 1), xylE under the control of the S. aureus hrtAB promoter (2), or xylE under the control of the S. aureus hrtAB promoter containing the indicated DR mutations (3–10; mutations are in grey) were grown in BHI or BHI + 2 µM hemin. Reporter activity was measured and is expressed as the percent of hemin-induced activity observed for the wildtype hrtAB promoter. All results are representative of at least three independent experiments. Error bars correspond to one standard deviation from the mean of triplicate samples within the same experiment; asterisks denote statistically significant differences by Student’s t test (p<0.05).