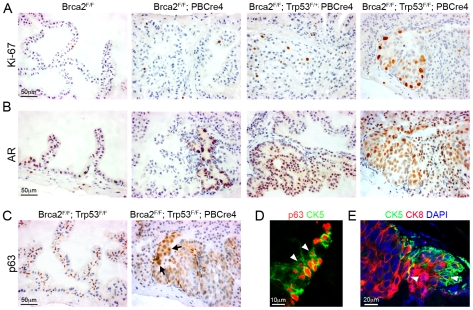
Figure 4. Brca2;Trp53 mutant prostates have hallmarks of cancer.
(A) Ki-67 immunohistochemistry shows increased proliferation in areas of LG PIN in Brca2F/F;PBCre4 and Brca2F/F;Trp53F/+;PBCre4 mutant prostates, a low number of proliferating cells are present in control (Brca2F/F) prostates. Brca2F/F;Trp53F/F;PBCre4 mutants have a large number of proliferating cells in areas of HG PIN. (B) AR immunohistochemistry demonstrating increased levels of expression throughout the nucleus and cytoplasm in areas of LG PIN in Brca2F/F;PBCre4 and Brca2F/F;Trp53F/+;PBCre4 mutant prostates, compared to control prostates (Brca2F/F). Brca2F/F;Trp53F/F;PBCre4 mutants have increased AR expression predominantly in the nucleus of cells in areas of HG PIN. (C) p63 immunohistochemistry shows an increase in p63-expressing cells in HG PIN lesions in Brca2F/F;Trp53F/F;PBCre4 mutant prostates and normal expression in the basal cells of control (Brca2F/F;Trp53F/F) prostates. Arrows indicate a cluster of abnormal p63-expressing cells that are rounder and nearer the lumen. (D) Left panel shows p63 (red) and CK5 (green) fluorescent immunohistochemistry analysis with labelled cells protruding into the lumen (white arrowheads) in a region of PIN in Brca2F/F;Trp53F/F;PBCre4 mutants. Right panel shows CK5 (green, basal cells) and CK8 (red, luminal cells) fluorescent immunohistochemistry with PIN lesions in Brca2F/F;Trp53F/F;PBCre4 mutants displaying an increase in luminal cells next to clusters of basal cells. White arrowhead marks CK5 and CK8 double-labelled cells. DAPI nuclear stain is blue. The anterior prostates of 16-month-old animals are shown.