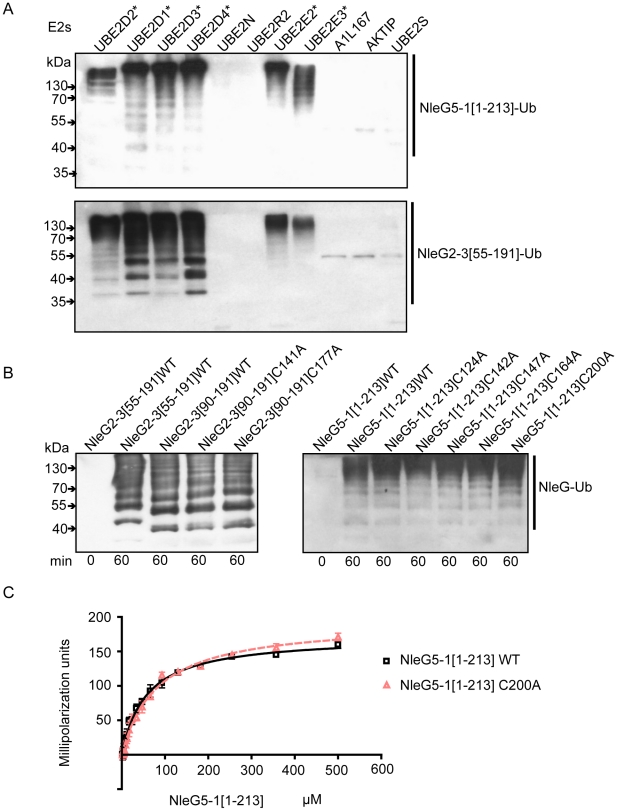
Figure 5. Interaction of NleG2-3 and NleG5-1 with human E2 enzymes.
(A) Western blot analysis of reactions using anti-ubiquitin antibodies performed in presence of ATP, ubiquitin, E1, the indicated human E2 enzymes and either NleG5-1[1–213] (top panel) or NleG2-3[55–191] (bottom panel). Reactions were performed at 30°C for 2 hours. The asterisk indicates the E2 enzymes supporting formation of multiple ubiquitinated protein species. The E2 nomenclature is in accordance with that used by the Human Genome Organization (http://www.genenames.org/genefamily/ube2.php). (B) Immunoblot analysis using anti-ubiquitin antibodies of reactions performed in the presence of ATP, ubiquitin, E1, UBE2D2 and NleG2-3 (left) or NleG5-1 (right) variants. The NleG2-3 variants include the wild type (WT) fragments NleG2-3[55–191] and NleG2-3[90–191] and C141A and C177A mutants of NleG2-3[90–191]. The NleG5-1 variants included wild type NleG5-1[1–213] and its C124A, C142A, C147A, C164A and C200A mutants. The samples were incubated at 30°C for the times indicated at the bottom of the panel. (C) Determination of dissociation constants of UBE2D2 with NleG5-1[1–213] wild type (WT) or its C200A variant. The change in fluorescence polarisation of fluorescein-labeled UBE2D2 is plotted as a function of NleG5-1 concentration with error bars indicating one standard deviation.