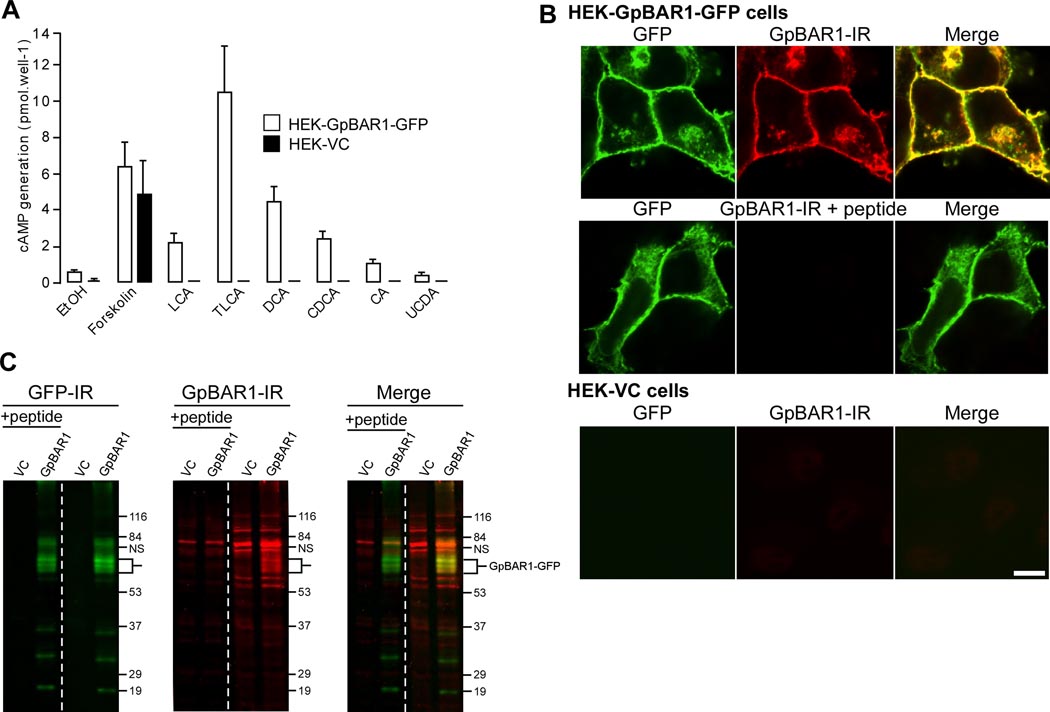
Figure 1. GpBAR1 antibody characterization.
A. BA-stimulated cAMP generation. HEK-GpBAR1-GFP and HEK-VC cells were incubated with vehicle (0.1% ethanol, EtOH), forskolin (10 nM) or BAs (100 µM) for 5 min. cAMP generation is expressed in pmol per well (n=6). B. Localization of GpBAR1-IR by immunofluorescence. In HEK-GpBAR1-GFP cells, GFP and GpBAR1-IR colocalized at the plasma membrane and in vesicles (upper row). Preadsorption (+ peptide) abolished signal for GpBAR1-IR but not GFP (middle row). Neither GFP nor GpBAR1-IR was detected in HEK-VC cells (bottom row). Scale bar = 10 µm. C. Detection of GpBAR1-IR by Western blotting. Membranes from HEK-GpBAR1-GFP or HEK-VC cells were separated by SDS-PAGE. The same blot was probed with antibodies to GFP (left) or GpBAR1 (middle) (right lanes) or preadsorbed antibody to GpBAR1 (left lanes, + peptide). Merged images are in right panel. In membranes from HEK-GpBAR1-GFP cells, antibodies to GFP and GpBAR1 detected proteins of ~60–70 KDa, corresponding to the GpBAR1-GFP fusion protein (merged). In membranes from HEK-VC cells, GFP-IR was undetectable and GpBAR1-IR was markedly diminished. Preadsorpion of GpBAR1 antibody did not affect GFP-IR but suppressed GpBAR1-IR.