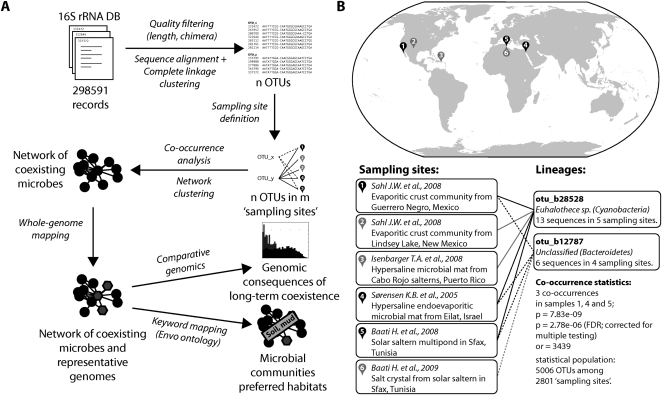
Figure 1.
Detection of coexisting microbial lineages. (A) Schematic description of the analysis procedure. Publicly available 16S ribosomal RNA sequences are first grouped into operational taxonomic units (OTUs), then annotated according to unique environmental sampling events, and finally searched for statistically significant co-occurrences. Where available, completely sequenced genomes are mapped onto the resulting network, which is then clustered and annotated. (B) Example for a specific lineage association. The two lineages (defined at a 97% 16S sequence identity cutoff) have been sampled overall relatively rarely, but they occurred together three times, at three distinct sites. (or) Odds ratio. Under “Sampling sites,” the investigative work of “Baati H. et al., 2009” refers to R Amdouni, E Ammar, H Baati, N Gharsallah, and A Sghir (unpubl.).