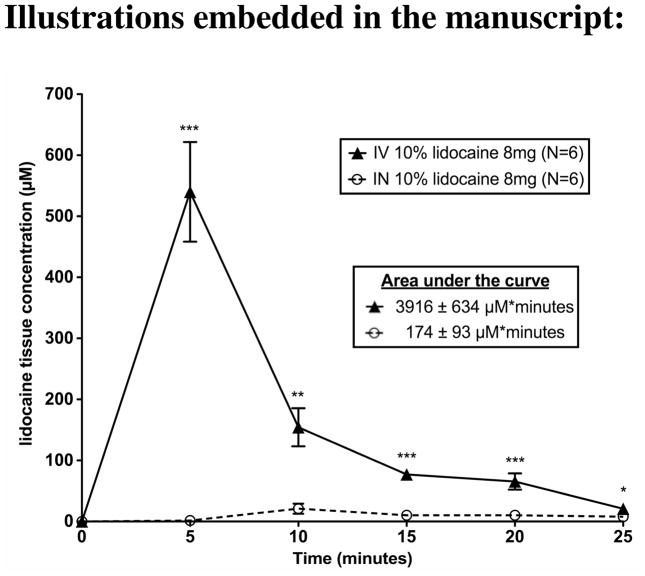
Figure 1. Intranasal administration of lidocaine leads to less drug delivery to the blood as compared to intravenous administration.
Following intranasal or intravenous delivery of 8 mg of 10% lidocaine, lidocaine concentrations in the blood were measured every 5 minutes. For intranasal delivery the area under the curve of lidocaine concentration in the blood over the 25 minute period was 174±93 μM*seconds, and intravenous delivery had an area under the curve of 3916±634 μM*seconds. Intranasal delivery had significantly less lidocaine from 0–25 minutes compared to IV delivery (p<0.001). The points and error bars represent the mean ± SEM (N=6). P values are represented as follows: <0.05 (*), <0.01 (**), and <0.001(***).