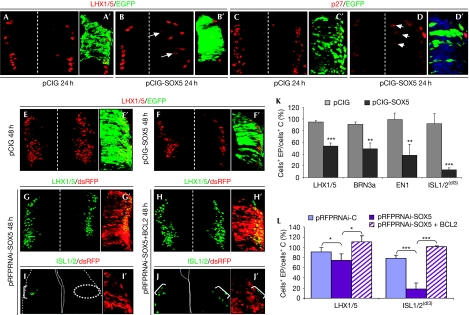
Figure 5.
Downregulation of SOX5 expression is required for the progression of dorsal interneuron differentiation. (A–D′) Sustained elevation of SOX5 in stage HH14–16 embryos induces ectopic activation of LHX1/5 (arrows; B,B′) and p27kip1 (arrows in D,D′) in neurons before they reach the mantle zone, with respect to control pCIG cells (A,A′, C,C′). (E,F,K) At stages HH18–22, there was a reduction in the number of LHX1/5+ (F,F′), BRN3a+, EN1+ and ISL1/2+ interneurons (K). (G,I,L) At stages HH18–22, knocking down SOX5 expression (mi2, red) affects the number of LHX1/5+ (G,G′,L) and ISL1/2+ interneurons (I,I′,L). (H–J,L) Co-electroporation with BCL2 rescues the total number of (K) LHX1/5+ and (brackets in L) ISL1/2+ interneurons. Quantification of the number of cells expressing a given neuronal marker at 48 h PE with the indicated construct. *P<0.05; **P<0.003; ***P<0.001. C, control; EP, electroporation; HH, Hamburguer and Hamilton; ISL1/2, islet 1/2; pCIG, pCAGGS-IRES-GFP; PE, post-electroporation.