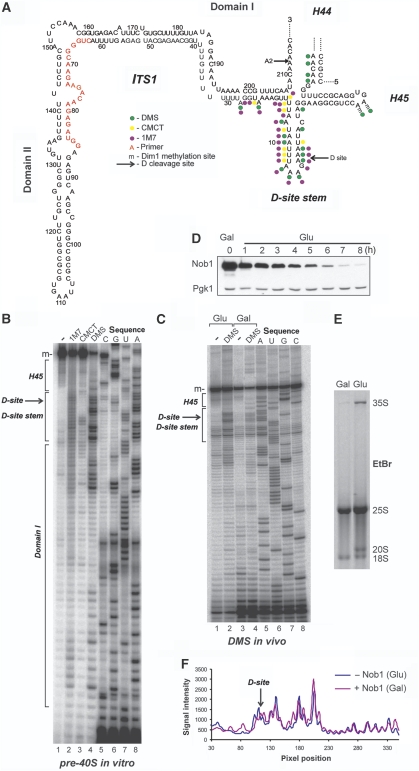
Figure 4.
At steady state the stem structure containing the D-cleavage site is highly flexible and unbound by proteins. (A) Overview of the chemical foot-printing results on a secondary structure of ITS1, including the 5′ end of the 18S rRNA, adopted from Yeh et al (1990). Red nucleotides indicate the location of the reverse transcriptase primer. Adenosines in H45 dimethylated by Dim1 in vivo are indicated with ‘-m'. Green circles indicate the nucleotide modified by DMS. Yellow and purple dots indicate the CMCT and 1M7-modified nucleotides, respectively. (B) The D-site region in purified 20S pre-rRNA is flexible and unbound by proteins. DMS, CMCT and 1M7 modification of RNA was performed at 30°C on purified pre-40S complexes isolated using plasmid-expressed HTP-tagged Nob1 as bait. All chemicals primarily modified nucleotides in the D-site stem region, indicating it is flexible or single stranded, whereas other regions predicted to be double stranded (i.e. H45 and Domain I) were largely protected from chemical modification. Adenosines in H45 dimethylated by Dim1 in vivo are indicated with ‘-m'. (C–F) The D-site helix is highly flexible and likely unbound by Nob1 in vivo. In vivo DMS was performed at 30°C on total RNA purified from GAL::3HA-nob1 cells (E) grown in glucose for 8 h (C, lanes 1 and 2) or galactose (C, lanes 3 and 4). Depletion of Nob1 was confirmed by western blotting (D) using an HRP-conjugated anti-HA antibody (Santa Cruz) and accumulation of 20S pre-rRNA was detected by ethidium bromide staining of total RNA in an agarose gel. Pgk1 antibodies (Santa Cruz) were used to confirm loading of equal amounts proteins on each lane (D). After primer extension, radiolabelled cDNAs were resolved on 12% polyacrylamide/7 M urea gels and visualized by autoradiography. Adenosines in H45 dimethylated by Dim1 in vivo are indicated with ‘-m'. Quantification of chemical probing data (F) was performed as described in the main text.