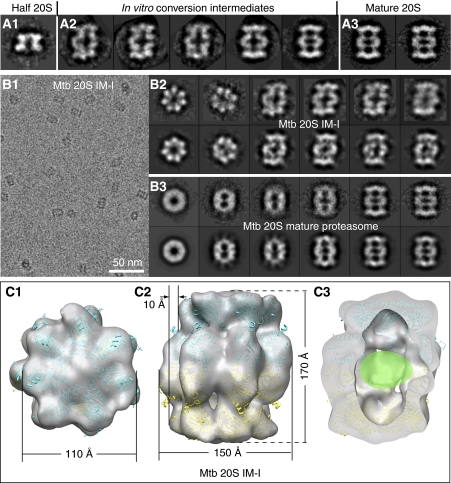
Figure 2.
A novel proteasome assembly intermediate as shown by cryo-EM and image classification. (A) A comparison of the side views of the freshly purified Mtb WT half proteasome (left panel, A1); in vitro conversion intermediates (middle panel, A2); and the fully assembly mature Mtb 20S proteasome (right panel, A3). (B) Cryo-EM characterization of the inhibitor-treated and in vitro assembled 20S proteasome intermediate (20S IM-I). The left panel (B1) shows a raw micrograph of the 20S IM-I embedded in vitreous ice, and the right panels show the reference-free 2D averages of the 20S IM-I (B2, top) and the purified 20S mature particles (B3, top). The corresponding reprojections from the 3D reconstructions are shown in the bottom panels for comparison (b2 bottom, the Mtb 20S IM-I; b3 bottom, the Mtb 20S mature proteasome). (C) Surface-rendered, 20% transparent top, side, and cut-open views of the cryo-EM map of the Mtb 20S IM-I at ∼25 Å resolution. The atomic model of the half 20S, derived from docking the α- and β-subunits into 3D cryo-EM map of the Mtb half proteasome, fits well in the density of the Mtb 20S IM-I. The β-propeptide densities, not resolved in the low-resolution map, is likely inside the central chamber, as indicated by a green oval in (C3).