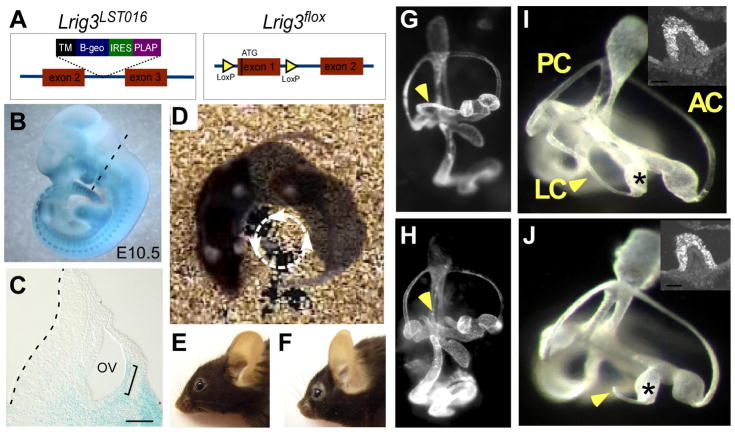
Fig. 2. Lrig3 mutant mice exhibit circling behavior due to a truncation of the lateral semicircular canal.
(A) Diagrams of two independent alleles of Lrig3 illustrating insertion of the gene trap vector in LST016 mice (left) and the introduction of LoxP sites on either side of the ATG-bearing exon in the conditional Lrig3flox allele (right). (B,C) X-gal detection of the Lrig3-β-geo fusion protein in an E10.5 Lrig3 heterozygous embryo (B) and in sections through the otic vesicle (C) in the plane indicated (dotted line, B). β-galactosidase activity is high in somitic mesoderm, the branchial arches and the limb buds. In the developing inner ear, transcription of Lrig3 is enriched in the lateral otic epithelium by E10.5 (bracket). Scale bar: 50 μm. (D) A single Lrig3 mutant mouse photographed in three points of its circling trajectory. (E,F) Lrig3 homozygotes (F) have shortened snouts compared to heterozygotes (E). (G–J) Paintfilled inner ears of E14 Lrig3 +/− (G,I) and −/− (H, J) embryos. Low magnification views of the entire inner ear (G,H) reveal a truncation of the lateral semicircular canal (arrowhead, H). Other structures appear normal in size and shape. High magnification views of the vestibular apparatus confirm truncation of the lateral canal (LC) but not the anterior (AC) or posterior (PC) canals. The lateral ampullae (asterisks) are unaffected, with no change in the number or distribution of MyosinVIIa-positive hair cells in the lateral cristae (insets). Dorsal is up; posterior is to the left.