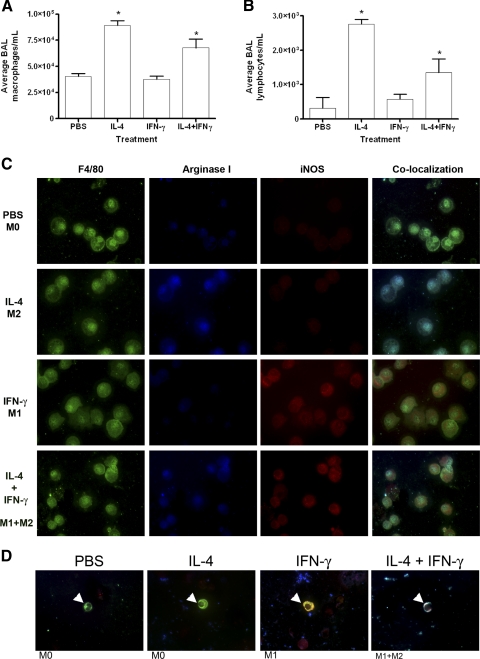
Figure 2.
Changes in BAL cellular composition and in the polarization of BAL macrophages and BDMCs upon exogenous pulmonary IL-4 and IFN-γ administration. Pulmonary macrophages (A) and lymphocytes (B) increase after IL-4 or IL-4 + IFN-γ administration by microspray into the trachea. Data represent the mean ± sem; n = 5; *, P < 0.001, compared with PBS- and IFN-γ-treated mice. (C) BAL macrophages (F4/80, green) were immunostained for arginase I and iNOS. Exposure to PBS resulted in an argIlowiNOSlow phenotype. Exposure to IL-4 induced arginase I (blue) but not iNOS, indicating M2 polarization. Exposure to IFN-γ induced iNOS (red) but not arginase I, indicating M1 polarization. Intrapulmonary administration of IL-4 and IFN-γ resulted in an argIhighiNOShigh phenotype. (D) Co-localized images of BDMCs (CD68, green, white arrowheads) express iNOS after pulmonary IFN-γ instillation, arginase I after IL-4 instillation, and iNOS and arginase I when instilled with both cytokines.