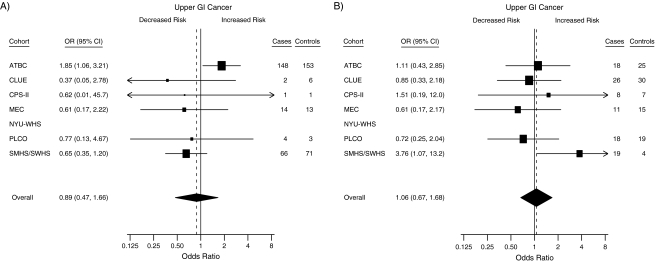
Figure 1.
Forest plots for the meta-analysis of the association between circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) and the risk of esophageal and gastric cancer within the Cohort Consortium Vitamin D Pooling Project of Rarer Cancers. Risk estimates, by cohort, for subjects with circulating 25(OH)D concentrations of A) <25 nmol/L and B) ≥75 nmol/L compared with the referent group (50–<75 nmol/L). Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were derived from conditional logistic regression models. The boxes show the odds ratios, the bars show the 95% confidence intervals, and the size of each box is inversely proportional to the variance of the log odds ratio estimate in each cohort. The overall estimates (diamonds) were derived from a meta-analysis using random-effects modeling. No estimates are given for the NYU-WHS because of small numbers in the exposed group. For the <25 nmol/L comparison, I2 was 39%; for the ≥75 nmol/L comparison, I2 was 9%. ATBC, Alpha-Tocopherol, Beta-Carotene Cancer Prevention Study; CPS-II, Cancer Prevention Study II Nutrition Cohort; GI, gastrointestinal; MEC, Multiethnic Cohort Study; NYU-WHS, New York University Women's Health Study; PLCO, Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial; SMHS/SWHS, Shanghai Men's Health Study/Shanghai Women's Health Study.