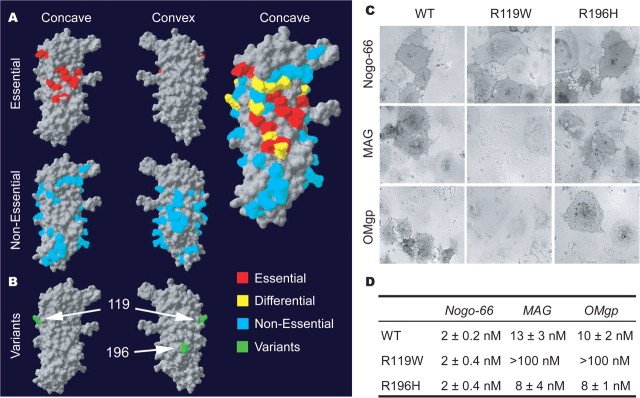
Figure 5.
Ligand-binding domain in NgR1 and the effect of schizophrenia-derived sequence variants. A, The human NgR1 surface required for ligand binding is summarized from previous analysis of 74 Ala substitution variants (Park et al., 2006; Laurén et al., 2007). Residues required for Nogo-66, MAG, and OMgp are highlighted in red, and residues required for one ligand but not all are shown in yellow. B, Location of the two separate coding region variants identified in an Italian population (green) (Sinibaldi et al., 2004). The R119 residue is at the edge of the region required for ligand binding. The R196 residue is centered on the convex surface not implicated in ligand binding. C, Binding of AP-tagged myelin ligands to WT-NgR1, NgR-R119W, and NgR-R196H variants. Pictures shown are at the Kd for each ligand for WT-NgR. Note the absence of binding of AP-MAG and AP-OMgp to R119W-NgR. D, AP-Nogo-66, AP-MAG, and AP-OMgp binding assays were conducted over a range of ligand concentrations, and bound AP was measured.