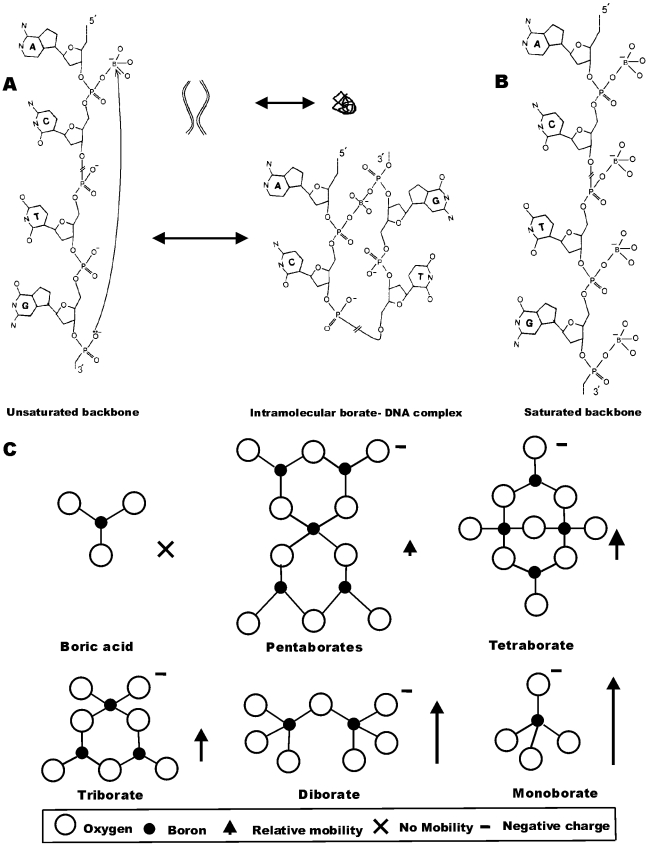
Figure 1. Guiding premise of the experiments and comparison of various polyborates.
(a) Intra-molecular Lewis acid complex formation between boronic species and non-vicinal phosphate groups, located far apart on DNA backbone, leads to a lower gel apparent length. A structural diagram of a region of a single strand of duplex DNA and a smaller schematic cartoon of two duplex DNA fragments illustrate the molecular and topological consequences of complexation. Additional complexes, not depicted here, form due to hydroxyl groups in agarose matrices; in such gels, DNA-borate-agarose complexes are expected. (b) Saturation of DNA backbone with the boronic species prevents intra-molecular Lewis acid complexation. (c) Polyborates are formed at high boric acid concentrations. Mass-to-charge ratio increases and electromobility decreases (denoted by upward arrow) with the number of borates in each complex.