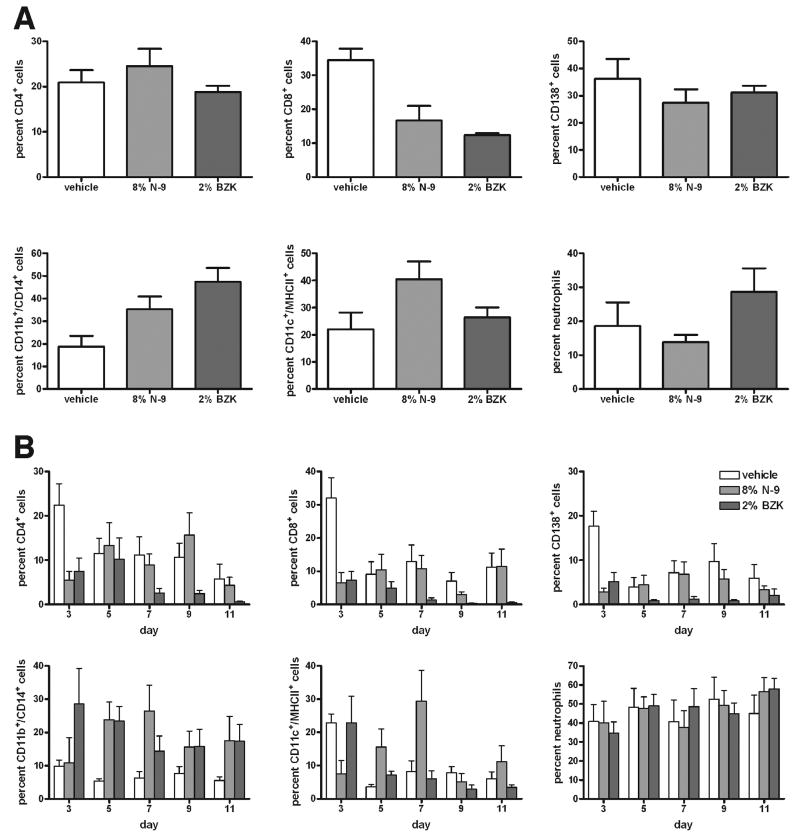
Figure 5.
Flow cytometry analysis of cells prepared from the rabbit vagina by (A) enzymatic lysis of vaginal tissue samples at day 11, and (B) minimally invasive cytobrush sampling of the vaginal surface at days 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11 after study initiation. Animals had been treated intravaginally with vehicle alone, 8% N-9, or 2% BZK. Live cells were analyzed by viability staining. Lymphocytes were identified by low forward/low sideward scatter, and percentages of CD4+ T lymphocytes, CD8+ T lymphocytes, and CD138+ B2 lymphocytes are shown. Large cells were identified by high forward/low sideward scatter, and percentages of CD11b+/CD14b+ macrophages and CD11c+/MHCII+ dendritic cells are shown. Neutrophilic granulocytes were identified by their low forward/high sideward scatter, and the percentage of viable cells is shown. The percentage of CD8+ cells decreased after treatment with N-9 and BZK in the tissue lysate cells (A), as well as on the vaginal surface (B), while the percentage of CD11b+/CD14+ macrophages increased both in the vaginal tissue lysate cells (A) and on the vaginal surface (B). One of two experiments is shown (n=2), with 7 animals per group.