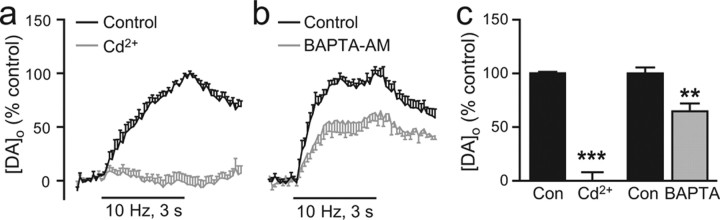
Figure 3.
Ca2+ entry and intracellular Ca2+ facilitate somatodendritic DA release. a, Average [DA]o versus time profiles evoked by local stimulation (30 pulses, 10 Hz) in the SNc in the absence and presence of a nonselective Ca2+ channel blocker, Cd2+ (100 μm, n = 6). b, Average [DA]o versus time profiles in SNc in the absence and presence of a fast-acting Ca2+ chelator BAPTA-AM (BAPTA) (50 μm, n = 6). c, Summary of the effect of Cd2+ and BAPTA on peak [DA]o; evoked [DA]o was measured at the time point of control peak [DA]o, which was taken as 100%. Blockade of stimulus-induced Ca2+ entry by Cd2+ abolished evoked [DA]o (n = 6, ***p < 0.001 vs control), confirming that Ca2+ entry is required to trigger evoked somatodendritic DA release. Buffering of stimulus-induced intracellular Ca2+ by BAPTA decreased evoked [DA]o (n = 6, **p < 0.01 vs control), demonstrating the involvement of intracellular Ca2+ elevation in evoked somatodendritic DA release.