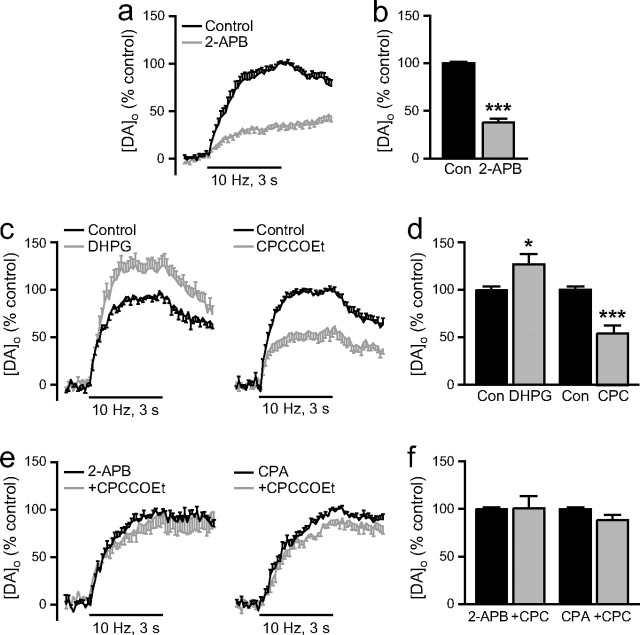
Figure 5.
Regulation of somatodendritic DA release by mGluR1 activation of IP3R-gated intracellular Ca2+ stores. a, Average [DA]o versus time profiles in SNc evoked by local stimulation (30 pulses, 10 Hz) in the absence and presence of a membrane-permeable IP3R inhibitor, 2-APB (left) (100 μm, n = 8). b, Summary of the effect of 2-APB on peak [DA]o; control peak [DA]o (Con) was taken as 100%. Inhibition of IP3Rs by 2-APB decreased evoked [DA]o (n = 8, ***p < 0.001 vs control), indicating involvement of Ca2+ mobilization from IP3R-gated stores in somatodendritic DA release. c, Average [DA]o versus time profiles in SNc in the absence and presence of an mGluR1 agonist DHPG (left) (1 μm, n = 8) or the mGluR1 antagonist CPCCOEt (right) (100 μm, n = 9). d, Summary of the effect of DHPG and CPCCOEt (CPC) on peak [DA]o; control peak [DA]o was taken as 100%. Activation of the IP3R-dependent mGluR1 pathway by DHPG significantly increased evoked [DA]o (n = 8, *p < 0.05 vs control), implicating a role for mGluR1-gated Ca2+ stores in somatodendritic DA release. Blockade of mGluR1s with CPCCOEt decreased evoked [DA]o (n = 9, ***p < 0.001), indicating that endogenously released glutamate normally facilitates somatodendritic DA release via activation of mGluR1s. e, Average [DA]o versus time profiles in SNc with CPCCOEt (100 μm) after pretreatment with the IP3R antagonist 2-APB (left) (100 μm, n = 6) or the SERCA inhibitor CPA (right) (30 μm, n = 6). f, Summary of the effect of CPCCOEt in 2-APB or CPA on peak [DA]o; control peak [DA]o in either 2-APB or CPA alone was taken as 100%. Suppression of evoked [DA]oby CPCCOEt was prevented by pretreatment with 2-APB (n = 6, p > 0.05, CPC + 2-APB vs 2-APB alone) or CPA (n = 6, p > 0.05, CPC + CPA vs CPA alone), demonstrating that activation of mGluR1s by endogenously released glutamate involves mobilization of Ca2+ from IP3R-gated ER stores.