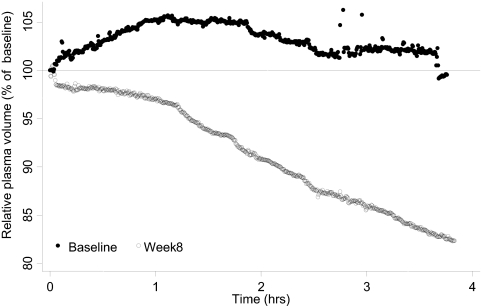
Figure 1.
Example of RPV monitoring as an indicator of dry-weight. A 42-year-old black man with ESRD on chronic hemodialysis for 8 years treated with four antihypertensive medications consented to participate in the DRIP trial after he was noted to be hypertensive. Interdialytic ambulatory BP monitoring revealed a BP value of 149/89 mmHg. At baseline, RPV monitoring demonstrated no change in RPV. Dry-weight was probed in the subsequent 8 weeks. He lost 2.0 kg of postdialysis weight from 62.0 to 60.0 kg. At 8 weeks, RPV monitoring revealed a 3.15% reduction in RPV per hour. Interdialytic ambulatory BP improved to 125/77 mmHg. RPV monitoring may be a useful tool to assess dry-weight.