Figure 2.
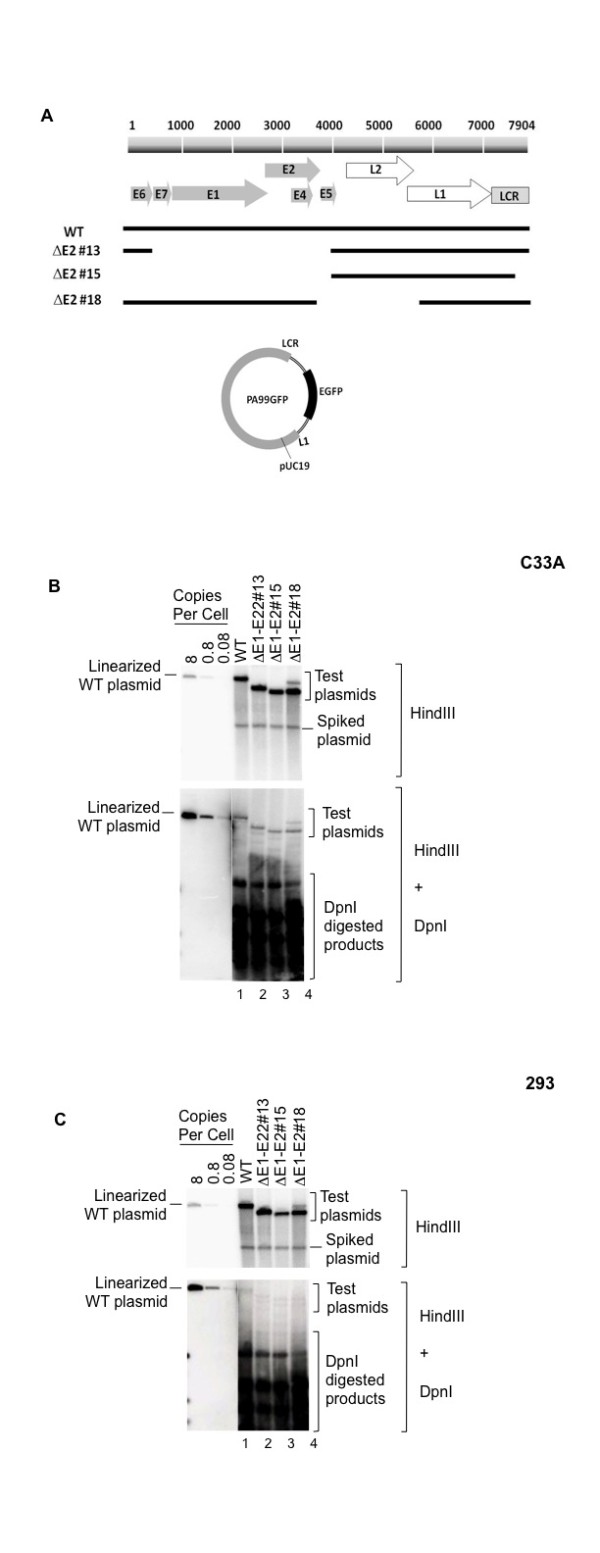
Replication of HPV16 DNA independently of E1 and E2 proteins. (A) Maps of PA99GFP and its mutant derivatives. The top bar represents a linear map of the HPV16 genome with responsive eight ORFs shown in arrows and the LCR indicated by a gray bar. The lines below show HPV16 segments, designated wild type (WT) and respective deletion mutants. PA99GFP contains an entire HPV16 DNA, an enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) under a CMV promoter in a pUC19 backbone. The mutants ΔE1-E2-#13, ΔE1-E2#15, and ΔE1-E2#18 harboring HPV16 DNA sequenced denoted by solid bars were created from pPA99GFP as described in Materials and Methods. Autoradiograms of representative Southern blots show extrachromosomal DNA (HindIII-digested products) and replicated DNA (DpnI-resistant) from transient replication assays with WT HPV16 and mutants in C33A (B) or 293 (C). Cells were transfected with WT or mutant HPV16 DNA containing plasmids as indicated. At 4 days post-transfection, extrachromosamal DNA were isolated from 1 × 107 cells. For Southern analysis, 10% of each sample was linearized with single cutting enzyme, HindIII and 90% was digested with HindIII and DpnI. Blots were hybridized with random-primed radiolabeled pUC19 DNA. The blots with HindIII digested DNA were exposed for 2 h whereas the ones with double digestion (HindIII + DpnI) were exposed for 4 days. The pUC19 backbone plasmid was used as the "spiked plasmid" to monitor the efficiency of plasmid recovery and completeness of DpnI digestion. The control DNA shown on the left, contains 1 ng,
