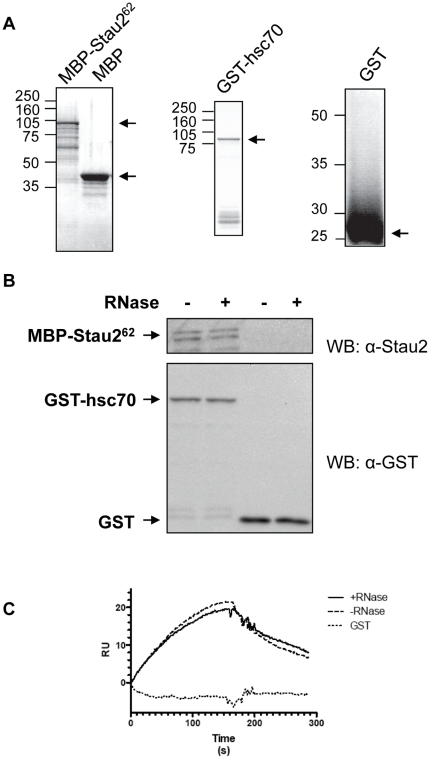
Figure 3. MBP-Stau262 binds GST-hsc70 through protein-protein interaction.
To confirm the RNA-resistant interaction between Stau2 and hsc70, bacterially expressed proteins were purified (A) and GST-pull down (B) and surface plasmon resonance SPR (C) assays were performed in the presence or absence of RNase A. (A) MBP-Stau262, MBP, GST-hsc70 and GST were purified on amylose and glutathione-Sepharose-4B affinity columns, respectively, and eluted proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie brilliant blue staining. (B) GST and GST-hsc70 were fixed on a glutathione-Sepharose-4B affinity column and MBP-Stau262 was loaded in the presence (+) or absence (−) of RNase A. After several washing, proteins were eluted from the columns and detected by western blotting using anti-Stau2 and anti-GST antibodies, respectively. (C) MBP and MBP-Stau262 were immobilized on different lanes of a SPR sensor chip. GST-hsc70 or GST were injected for 3 minutes over the surfaces in the presence or absence of RNase and then buffer alone was injected for 2.5 min to monitor protein dissociation rate. The resulting resonance units (RU) were measured during the association and dissociation phases. The baseline obtained with the MBP-coupled reference surface was subtracted from the sensorgram obtained from the MBP-Stau262-coupled surface and a typical result is shown.