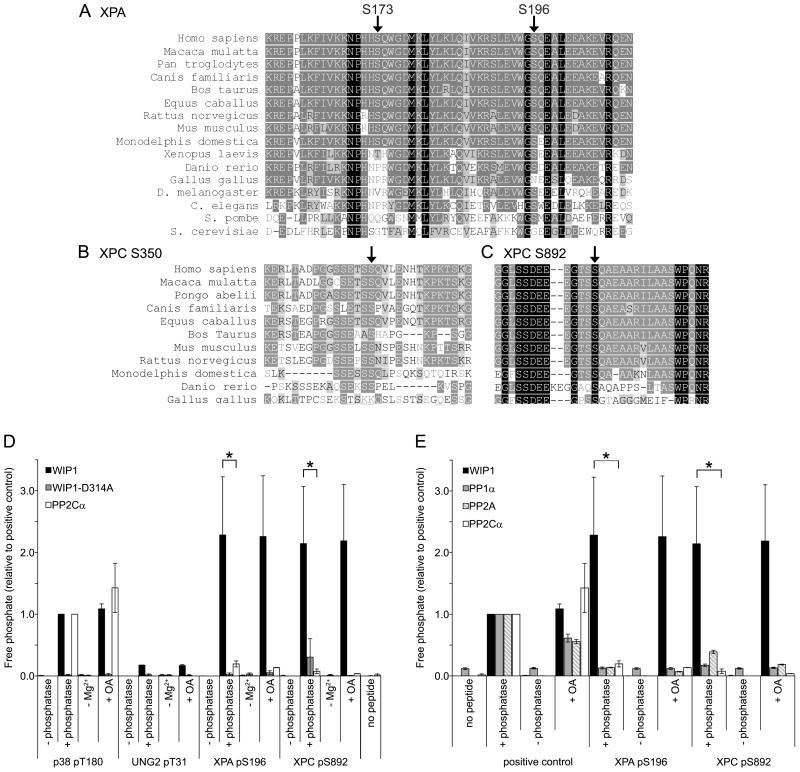
Figure 5.
XPA and XPC phosphopeptides are dephosphorylated by WIP1 in vitro. (A) Protein sequence alignment of various orthologues of XPA, containing serines 173 and 196, indicated by arrows. Identical amino acids are highlighted with a black background while conservative amino acid substitutions are indicated with a gray background. (B, C) Protein sequence alignment of various orthologues of XPC, containing serines 350 (B) and 892 (C), indicated by arrows. (D) XPA S196 and XPC S892 phosphopeptides are dephosphorylated by WIP1 in vitro. XPA pS196 and XPC pS892 phosphopeptides were incubated with human recombinant WIP1, phosphatase-dead WIP1-D314A, or PP2Cα protein. p38 pT180 and UNG2 pT31 phosphopeptides were used as a positive and negative control, respectively. −Mg2+ indicates incubation in the absence of magnesium and +OA indicates incubation with the PP1α and PP2A phosphatase inhibitor, okadaic acid. Free phosphate released from the phosphopeptide was measured by malachite green phosphate assay to determine relative phosphatase activities on each phosphopeptide. Error bars represent the standard error (n=3) and the asterisk indicates statistical significance (p<0.05). (E) WIP1, but not other serine/threonine phosphatases, dephosphorylates XPA S196 and XPC S892 phosphopeptides in vitro. XPA pS196 and XPC pS892 phosphopeptides were incubated with human recombinant WIP1, PP1α, PP2A, or PP2Cα protein. Positive controls were as follows: p38 pT180 for WIP1 and PP2Cα, CHK1 pS345 for PP1α, and the generic serine/threonine phosphopeptide, RRA(pT)VA, for PP2A. Phosphatase activity was measured as described above. Error bars represent the standard error (n=3) and the asterisk indicates statistical significance (p<0.05).