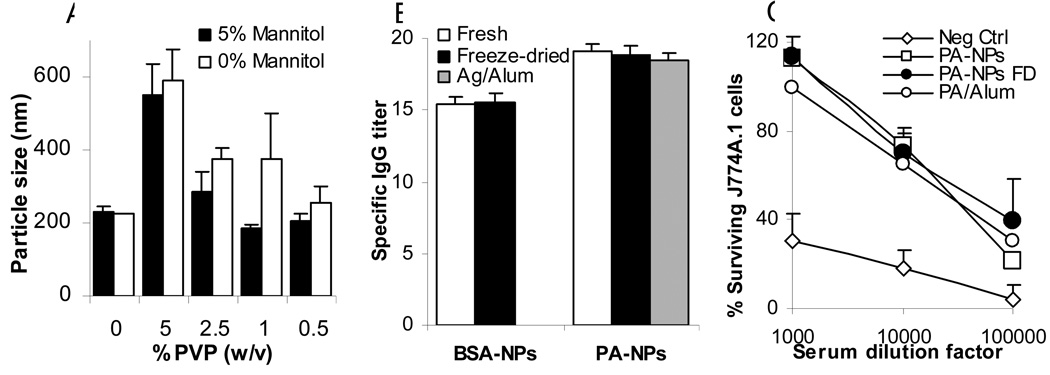
Figure 3. The lyophilization did not damage the immunogenicity of the antigens conjugated onto the surface of the nanoparticles.
(A) Lyophilization of the BSA-nanoparticles using both mannitol and PVP. (B) The lyophilized, antigen-conjugated nanoparticles (Freeze-dried) were as immunogenic as the freshly prepared ones (Fresh). BSA and protective antigen (PA) protein were used as model antigens. For the PA, a PA adsorbed onto Alum (Ag/Alum) group was included as a control. For each dosing, freshly prepared antigen-conjugated nanoparticles were lyophilized, immediately reconstituted with water to its original volume, and then injected into mice. Data are mean ± S.D. from 5 mice per group. (C) The anthrax lethal toxin neutralization activity of the serum samples from mice immunized with lyophilized/freeze-dried PA-NPs (PA-NPs FD) or freshly prepared PA-NPs. Neg Ctrl means un-immunized mice. Serum samples from mice in individual group were pooled, and the data reported were mean ± S.D. from 4 measurements.