Fig. 1.
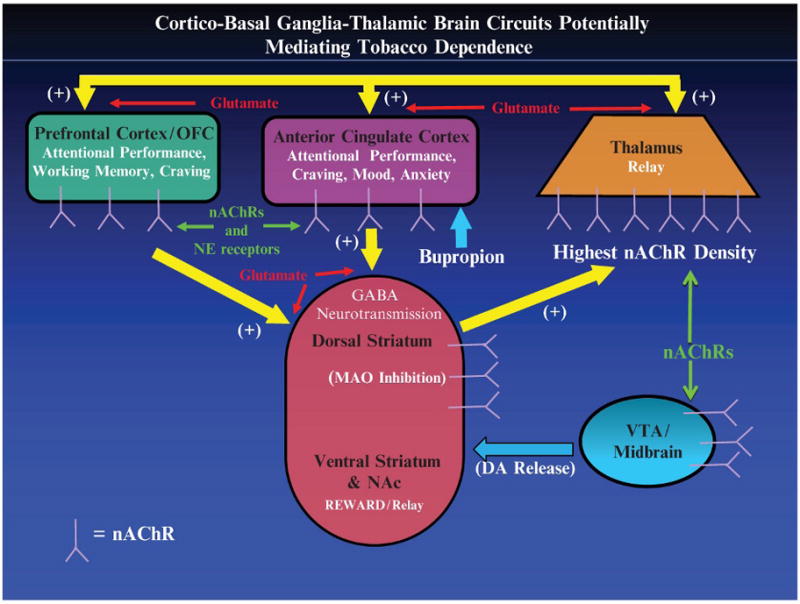
Representation of the cortico–basal ganglia–thalamic brain circuitry that may mediate the effects of nicotine/smoking on attentional control, craving, mood, and anxiety. Potential targets for nicotine/smoking to enhance attention (and improve craving, mood, and anxiety) include (1) direct stimulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) in cortex, (2) stimulation of the nAChR-rich thalamus and basal ganglia, (3) activation of dopaminergic mesolimbic reward pathways originating in the VTA and projecting to the striatum, and (4) monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibition in the basal ganglia. NAc nucleus accumbens; VTA ventral tegmental area
