Figure 3.
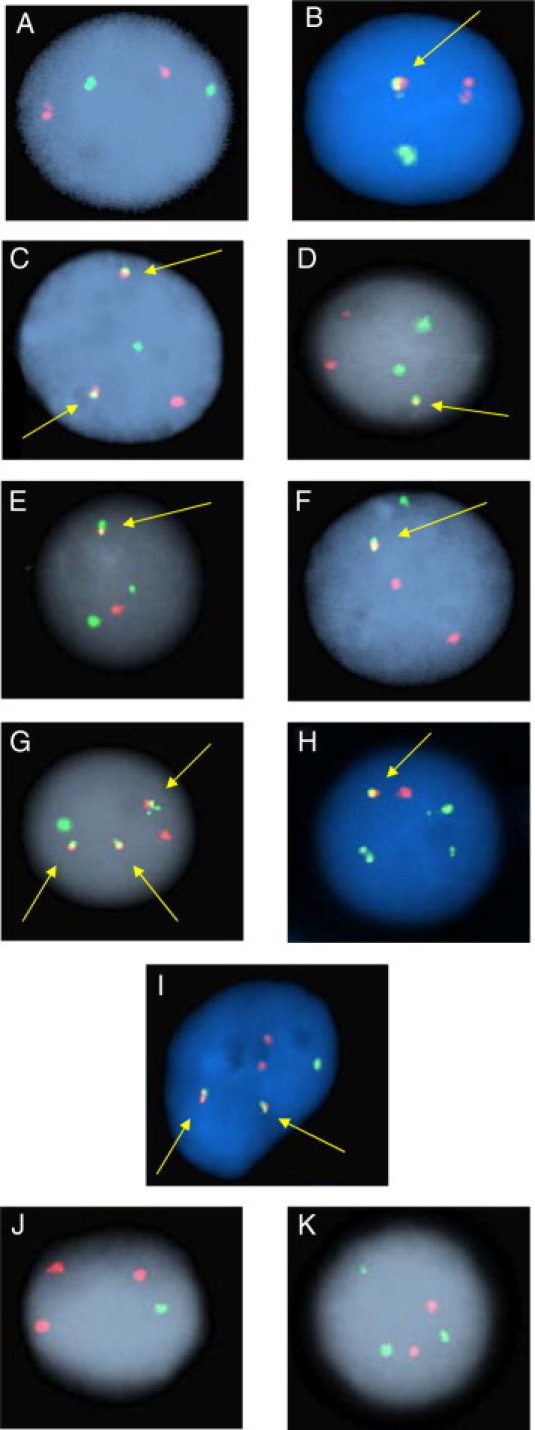
Representative interphase FISH signal patterns observed with the MLL/partner D-FISH assays. A: Nonneoplastic nucleus with a normal 2R2G signal pattern. B: Nonneoplastic nucleus with coincidental R and G signal overlap resulting in a 1R1G1F signal pattern. C: Neoplastic nucleus with a 1R1G2F signal pattern representing a balanced translocation resulting in two MLL/partner fusion signals. D: Neoplastic nucleus demonstrating a 2R2G1F signal pattern representing a complex translocation. E: Neoplastic nucleus demonstrating a 1R2G1F signal pattern indicating an unbalanced MLL/partner translocation with an associated deletion of the partner DNA at one of the translocation junctions. F: Neoplastic nucleus demonstrating a 2R1G1F signal pattern indicating an unbalanced MLL/partner translocation with an associated deletion of the MLL DNA at one of the translocation junctions. G: Neoplastic nucleus with a 1R1G3F signal pattern due to gain of an additional copy of one of the derivative chromosomes. H: Neoplastic nucleus with a 1R3G1F signal pattern indicating an unbalanced translocation and MLL duplication/trisomy of chromosome 11. I: Neoplastic nucleus with a 2R1G2F signal pattern indicating a balanced translocation and an additional copy of the partner chromosome. J and K: Abnormal signal patterns lacking a fusion (3R1G and 2R3G) are observed as a result of translocations that disrupt only one of the two genes covered by the probe set. The 3R1G signal pattern also denotes a deletion of 1 MLL signal. Arrows denote yellow fusion signals.
