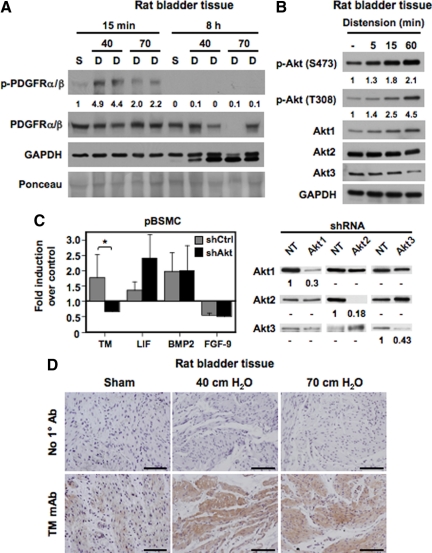
Figure 1.
Activation of the PDGFR ex vivo and in vitro induces TM expression in bladder SMC. A: Rat bladders were hydrodistended to 40- or 70-cm water pressure for the indicated times to promote injury. Nondistended bladders from sham-operated rats served as controls. Lysates from nondistended sham bladders (S) and distended organs (D) were immunoblotted with antibodies to total and phosphorylated (activated) PDGFRα/β or glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Tissues showed a rapid and transient phosphorylation of the PDGFR by 15 minutes following distension (compare 40- and 70-cm distension conditions at 15 minutes with nondistended controls). PDGFR activation disappeared by eight hours. No corresponding change in total PDGFR levels was observed with time. The values represent quantification of the increase in PDGFR phosphorylation. B: Lysates from rat bladders hydrodistended as in A for the indicated times were immunoblotted with antibodies to Akt1, Akt2, Akt3, Akt phosphorylated at Ser473 or Thr308, and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. The data indicate a time-dependent increase in Akt phosphorylation with bladder distension. The values represent quantification of the increase in Akt phosphorylation at S473 and T308. C: Populations of pBSMC infected with retroviruses expressing shRNAs against Akt1, Akt2, and Akt3 (black bars) or control nontargeting shRNA (gray bars) were exposed to PDGF treatment for four hours and changes in gene expression assessed by real-time RT-PCR analysis. The graph shows fold change in expression of the indicated genes with PDGF relative to vehicle control. Data represent the mean ± SD of two independent trials, in which samples were assayed in duplicate. Knockdown of Akt ablated PDGF-induced TM expression (P < 0.01), whereas expression of other genes such as LIF, BMP2, and fibroblast growth factor-9 (FGF-9) was not significantly changed by Akt knockdown. The panel on the right shows immunoblot analysis confirming specificity of Akt knockdown in stable populations of pBSMC following infection with retroviruses individually targeting the three Akt isoforms. The extent of knockdown is presented as signal remaining for each Akt isoform relative to nontargeting control. D: Sections from rat bladders distended ex vivo for eight hours to 40- or 70-cm water pressure were stained sequentially with anti-TM primary antibody and horseradish peroxidase-conjugated species-specific secondary antibody. Increased TM staining was evident in the detrusor smooth muscle of distended specimens but not of nondistended, sham-operated control bladders. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Scale bar = 100 μm.