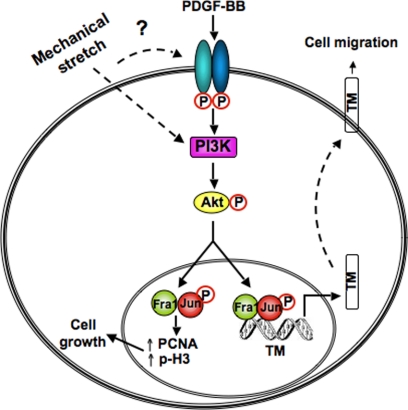
Figure 8.
A model of regulation of TM by the PDGFR axis in bladder smooth muscle. Exposure to PDGF in vitro or bladder wall distension in vivo causes phosphorylation and activation of the PDGFR, initiating downstream signaling cascades such as the PI3K/Akt pathway. PDGF-stimulated, PI3K/Akt-dependent signals activate specific AP-1 components (c-jun and Fra1), which bind to the TM promoter to increase its expression and thereby promote cell migration. PDGF also stimulates cell cycle transit in a Fra1-dependent manner.