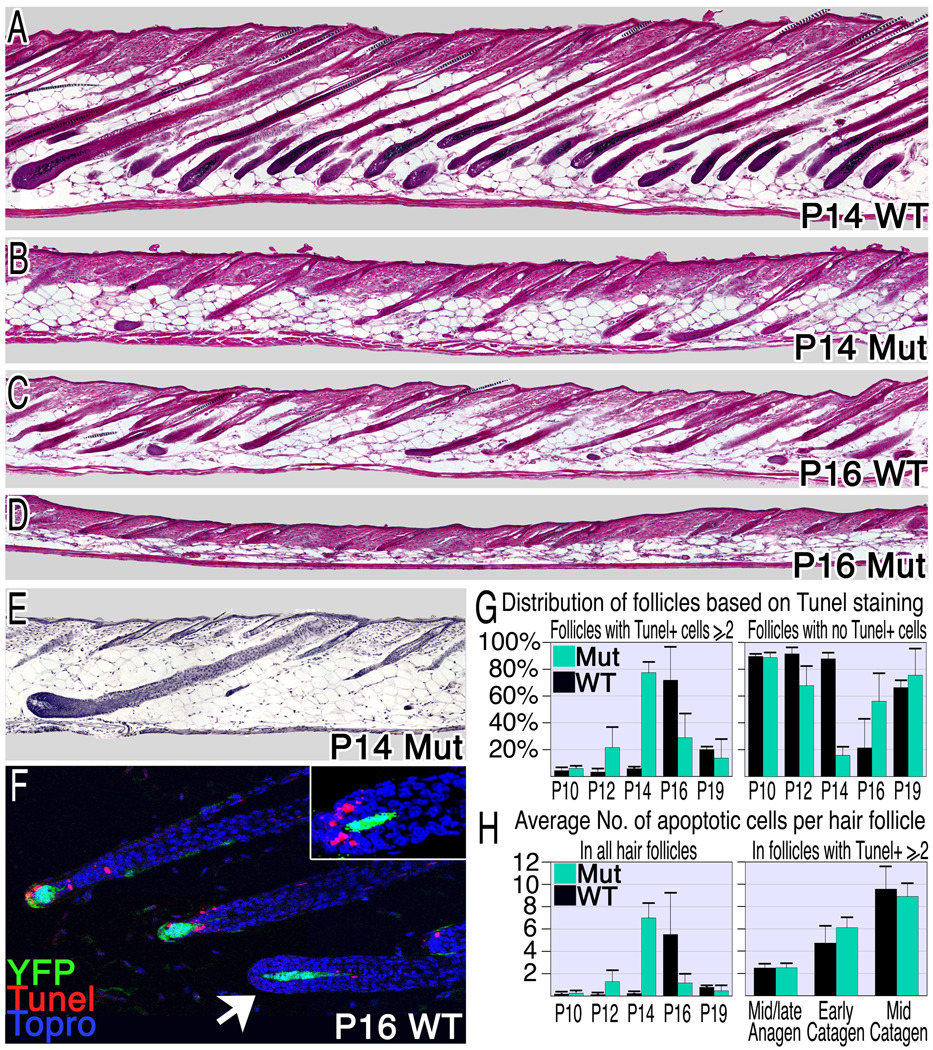
Figure 4. Compromising β-catenin in the DP induces premature catagen.
(A–D) Hematoxylin and eosin stained sections from wild type and mutant mice reveal premature and asynchronous induction of the catagen phase in mutant mice. (E) An anagen follicle surrounded by late catagen and telogen follicles in P14 mutant skin. (F–H) TUNEL analysis of apoptosis. Follicles in catagen exhibit 2 or more apoptotic cells, while the absence of apoptotic cells in the hair matrix or bulge was used as a marker for anagen or telogen follicles respectively. (F) TUNEL staining (red) of P16 wild type skin at catagen onset reveals the rapid transition from TUNEL negative follicles (arrowhead) to those with multiple apoptotic cells/follicle. YFP expression marks the DP (green) and nuclei are blue. Inset shows a follicle morphology typical of the transition from late anagen to early catagen where abundant TUNEL staining reveals entry to the catagen phase. Many catagen follicles were observed in mutant skin at P12 (G: left), 4 days earlier than wild type. However, anagen-follicles are still predominant at this stage (G: right). (H) The average number of apoptotic cells per hair follicle per section was calculated. On the left all follicles were included and on the right only those follicles that have entered catagen were scored to eliminate the diluting effects of follicles that remain in anagen. See also Figure S3.